26 July 2022: Articles 
Mass-Forming Gastric Heterotopia of the Rectum: A Series of 3 Cases from a Single Tertiary Health Center
Challenging differential diagnosis, Rare disease
Jeffrey D. Covington1ABDEF, Yang Zong1ABCDEF, Arslan Talat2BE, Cara Strock1BE, Keith Tomaszewicz1BCDE, Jaroslav Zivny2BE, Michelle X. Yang1ADE*DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.936631
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936631
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Gastric heterotopia is a benign entity found throughout the gastrointestinal tract but is rarely identified in the rectum. Since 1939, only 94 cases have ever been identified, and it can present as a mass formation with symptomatology that mimics colorectal malignancy. In some instances, malignancy has been shown to arise within rectal gastric heterotopia. Here, we present 3 cases from the past 20-year period of rectal gastric heterotopia at a single tertiary institution.
CASE REPORT: A 25-year-old man (case 1), a 58-year-old woman (case 2), and a 33-year-old man (case 3) were found to have polypoid mass-like lesions greater than 1.0 cm within the rectum. Following biopsy, pathology showed gastric oxyntic mucosa flanked by colorectal mucosa, thus indicating gastric heterotopia. Presenting symptoms from all patients consisted of unspecified anal pain, hematochezia, or a combination of both. All patients were treated with endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), which provided relief of symptoms and confirmed no evidence of invasive malignancy.
CONCLUSIONS: Rectal gastric heterotopia can mimic malignancy and in very rare instances can harbor high-grade dysplasia as well as invasive carcinoma. EMR seems to be a definitive treatment that offers relief to patient symptomatology and reassurance that any dysplasia is identified and removed.
Keywords: endoscopic mucosal resection, Gastric Mucosa, Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage, Rectum, Adult, Choristoma, Female, Humans, Male, Middle Aged, Rectal Diseases, Stomach Diseases
Background
Heterotopia is defined as ectopic tissue present in a location separate from its natural anatomic and normal developmental environment. Within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, gastric heterotopia has been identified in various sites such as in the nasopharynx [1], esophagus (inlet patch), gallbladder [2], bile duct [3], and in the ileum [4], including the Meckel’s diverticulum. Several studies have shown the prevalence of 0.4% [5] and 0.75%[6] of gastric heterotopia in the esophagus, and the prevalence of 0.51%[6] and 1.9% [7] of gastric heterotopia in the duodenum. However, of those studies, none have reported gastric heterotopia in the rectum or anus. Yu and coauthors stated that of the 3504 colonoscopy cases that were included in their study, gastric heterotopia was not seen in the colon [6]. A review of 158 cases of gastric heterotopia throughout the GI tract showed no instance of it being present in colorectal or anal mucosa [8].
Since the first case report of heterotopic gastric tissue of the rectum was published in 1939 [9], over the last 83 years, only 94 cases have been reported in the rectum and 8 cases in the anus [10,11]. Taken together, gastric heterotopia of the rectum is a rather rare finding, and mass-forming gastric heterotopia in the rectum is extremely rare, and as such may present a diagnostic challenge given its rarity. In order to add to the repertoire of cases of rectal gastric heterotopia, we present 3 cases from a single-institution general academic practice that presented over the last 20 years.
Case Reports
CASE 1:
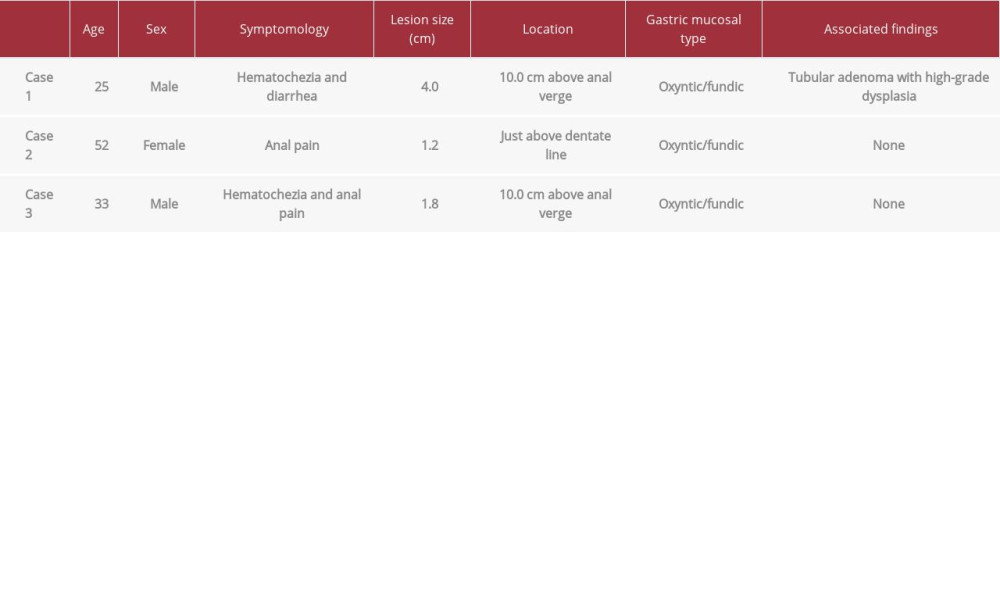
A 25-year-old man with several episodes of hematochezia presented to the gastroenterology clinic and was referred for colonoscopy. The inquiry of the past medical history and review of systems revealed he had a colonoscopy at the age of 3 due to chronic diarrhea with mucus and was diagnosed with nodular lymphoid hyperplasia of the colon. Since then, the patient had frequent bowel movements, up to 15 time per day, with loose stool and occasional small amount of blood. Physical exam and digital rectal exam were normal. The lab and imaging studies showed hypercholesterolemia and mild proximal septal hypertrophy without evidence of left ventricular out-flow tract gradient or obstruction. Colonoscopy and a lower endoscopic ultrasound revealed 2 masses in the middle rectum with isoechoic thickening of the mucosa and submucosa, measuring 4 cm and 1 cm in the greatest dimension, respectively. The larger mass extended from the anal verge about 10 cm proximally and was predominately on the lateral rectal wall, involving approximately one-half of the circumference of the rectum, with central umbilication, elevated scalloped border, and few superficial ulcerations (Figure 1). The smaller lesion was located directly opposite the larger mass, with an elevated nodular appearance and few superficial ulcerations.
The smaller lesion was found to have a tubular adenoma while the large mass showed tubular adenoma admixed with gastric oxyntic-type heterotopic mucosa. Immunohistochemical stains showed that the colonic mucosa was positive for CK20, CDX2, and SATB2, with rare positivity of CK7 (Figure 1). The gastric heterotopic mucosa was positive for CK20 in the surface foveolar epithelium, but negative for CK7, CDX2, and SATB2 (Figure 1). To ensure that a specimen or labeling error had not occurred, short tandem repeat PCR was performed to confirm that the gastric heterotopic tissue and colonic tissue both belonged to the same patient. These findings supported a diagnosis of mass-forming gastric oxyntic heterotopia within the rectum alongside a tubular adenoma.
EMR of both lesions was performed 5 months after the initial diagnosis. The lesion containing gastric heterotopia was found to contain a tubular adenoma with focal high-grade dysplasia within the colonic mucosa. The tubular adenoma was excised completely. The gastric heterotopic mucosa was shown to be of oxyntic type and was present focally at the cauterized resection margins.
CASE 2:
A 52-year-old woman with unspecified anal pain for several months and a non-contributory past medical history presented for gastroenterology clinical evaluation and colonoscopy. Physical exam was normal and digital rectal exam showed internal hemorrhoids. Colonoscopy and endoscopic ultrasound showed a 1.2-cm mucosal nodule just above the dentate line. The mucosa surrounding the nodule was thickened but did not appear to extend beyond the muscularis propria. Two months later, a flexible sigmoidoscopy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was performed. The entire lesion was excised and sent for pathological evaluation. Histological examination showed nodular gastric oxyntic mucosa confined to the lamina propria of colonic mucosa. The gastric heterotopic mucosa was present at the cauterized edge. No other pathological features were noted. The EMR of the lesion was the only treatment that the patient received and she was then lost to further follow-up.
CASE 3:
A 33-year-old man presented to his primary care physician with bright red blood per rectum and rectal pain. The digital rectal exam revealed non-thrombosed external hemorrhoids without any fissure or other lesion. The remaining physical exam and past medical history were non-contributory. The patient was treated with steroid suppositories with no relief in symptoms. The patient re-presented to his primary care physician 8 months later with continued bleeding and unbearable rectal pain with all bowel movements. The patient was referred to clinical gastroenterology for evaluation and a colonoscopy was performed. The initial colonoscopy showed a 1.8-cm umbilicated, sessile rectal polyp that was biopsied (Figure 1). Eighteen days later, a second colonoscopy was performed with endoscopic ultrasound and EMR. Ultrasound findings showed a heterogenous submucosal nodule within the sessile rectal polyp located 10 cm from the anal verge, with well-defined boarders. EMR was performed to completely excise the polypoid and submucosal nodular lesion. The biopsy from the initial colonoscopy showed gastric oxyntic mucosa. Histology of the EMR specimen showed heterotopic gastric oxyntic mucosa with no dysplastic or adenomatous features. Six months following the EMR, a follow-up colonoscopy was performed with a biopsy obtained of a 0.5-cm rectal nodule. Pathology showed normal rectal mucosa with no evidence of remaining gastric heterotopic mucosa. Two years after the EMR, a second follow-up colonoscopy was performed, showing normal colorectal mucosa and no biopsy specimens were obtained.
Discussion
Gastric heterotopic mucosa is ectopic gastric tissue existing outside of the stomach. Though much attention has been given to gastric heterotopia in the foregut and midgut, it is a very rare finding that can occur in the lower GI tract. Due in part to its rarity, rectal gastric heterotopia can be a diagnostic challenge. Here, we reported 3 cases of rectal heterotopic gastric mucosa (Table 1). Because it is such a rare finding, in our first case, we went to great effort to confirm that the correct patient and correct tissue were identified using short tandem repeat PCR to examine microsatellite polymorphism.
The etiology and mechanism behind the development of heterotopia is currently unknown, but 3 hypotheses have been offered to explain the phenomenon of gastric heterotopia. The most plausible hypothesis suggests that unknown conditions or injury develops that induces the pluripotent primitive endodermal stem cells lining the intestinal canal to differentiate. However, an error in differentiation may occur whereby the cells instead of differentiating into colorectal epithelium differentiate into gastric mucosal epithelium [12]. A second hypothesis suggests that following a destructive process of normal intestinal mucosa, abnormal regeneration of tissue facilitates a growth of gastric heterotopia. The conditions contributing to a replacement of normal mucosa with pure heterotopic gastric mucosa are not known and not universal following all injuries [13]. The third, and perhaps least plausible explanation of rectal gastric heterotopia suggests that as embryonic stomach tissue descends, nests of cells can remain arrested within the esophagus. Though this hypothesis might offer insight into the creation of an inlet pouch of the esophagus, it does not seem to explain the presence of rectal gastric heterotopia [14].
The first known case report of heterotopic gastric mucosa in the rectum was reported by Ewell and Jackson in 1939 in a 6-year-old boy [9]. This was followed by a second case published in France of a 23-year-old woman in 1955 [15] and a third case in 1960 [16]. Since then, several case reports have been presented in the literature. In 2016, Iacopini et al published a comprehensive review of all cases of heterotopic gastric mucosa in the rectum and anus, which included 68 evaluable cases in the rectum and 4 evaluable cases in the anus [10]. In 2018 Mannan et al performed a search across 23 years at 5 separate institutions, which revealed 26 additional cases in the rectum and 4 additional cases in the anus [11].
A significance of these findings is the associated symptomatology that rectal gastric heterotopia can present. In the review by Iacopini et al, anorectal symptoms, such as hematochezia and anal pain, were described in 69% of patients with heterotopic gastric mucosa in the rectum and anus [10]. Vague, nonspecific abdominal symptoms were found in 11% of patients [10]. In the study by Mannan et al, hematochezia was found in 30.7% of patients [11]. In reports by Srinivasan et al [17] and Steele et al [18] hematochezia and anal pain were the main presenting symptoms of rectal and anal gastric heterotopia. Of the 3 patients presented herein, 2 patients displayed hematochezia. One displayed hematochezia with painful defecation and the other had symptomatic diarrhea with hematochezia. The third patient did not have hematochezia or diarrhea but had unspecified anorectal pain.
In addition, prior studies have reported that heterotopic tissue within the gastrointestinal tract can harbor dysplasia and malignancy. Adenocarcinoma arising from gastric heterotopia has been described in the esophagus [19–21], jejunum [22], ileum [23], and colon [14]. Five cases of pyloric gland adenomas arising in rectal gastric heterotopia have been reported, with 2 of those cases harboring adenocarcinoma [11,24]. Our first case was found to have a tubular adenoma with focal high-grade dysplasia admixed with the mass forming gastric heterotopia. Given that 28.6% of rectal gastric heterotopia is found either in asymptomatic patients or incidentally during screening colonoscopy [10,11], it is particularly important to recognize this finding and adequately sample it for pathological examination.
Complete endoscopic mucosal resection or endoscopic submucosal dissection was shown to be a definitive treatment for rectal gastric heterotopic mucosa when found in the rectum. Our 3 cases ultimately had excision using endoscopic mucosal resection. Of the patients who had definitive follow-up in our cohort, no additional symptoms, complications, or issues were reported following the endoscopic mucosal resection.
Conclusions
In summary, gastric heterotopic mucosa is a very rare entity that can present a diagnostic challenge and carries a risk of malignancy. The symptomatology, which includes hematochezia and anal pain, can be nonspecific and overlap with other entities such as diverticular disease and anal fissures. Furthermore, some instances of gastric heterotopia in the rectum can be found asymptomatically and incidentally. Given the potential for symptoms to adversely affect the patient’s quality of life and the potential risk for malignant transformation, care should be taken not to overlook these findings in the lower GI tract. Endoscopic mucosal resection and submucosal resection for deep lesions seem to be effective treatments both in the patients presented here and in prior reports.
References:
1.. Wacrenier A, Fayoux P, Augusto D, Gastric heterotopia in the nasopharynx: Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2002; 64(1); 65-67
2.. Hayama S, Suzuki Y, Takahashi M, Heterotopic gastric mucosa in the gallbladder: Report of two cases: Surg Today, 2010; 40(8); 783-87
3.. Kalman PG, Stone RM, Phillips MJ, Heterotopic gastric tissue of the bile duct: Surgery, 1981; 89(3); 384-86
4.. Doberneck RC, Deane WM, Antoine JE, Ectopic gastric mucosa in the ileum: A cause of intussusception: J Pediatr Surg, 1976; 11(1); 99-100
5.. Fang Y, Chen L, Chen DF, Prevalence, histologic and clinical characteristics of heterotopic gastric mucosa in Chinese patients: World J Gastroenterol, 2014; 20(46); 17588-94
6.. Yu L, Yang Y, Cui L, Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract: Prevalence, histological features, and clinical characteristics: Scand J Gastroenterol, 2014; 49(2); 138-44
7.. Genta RM, Kinsey RS, Singhal A, Suterwala S: Hum Pathol, 2010; 41(11); 1593-600
8.. Terada T, Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract: A histopathologic study of 158 cases: Pathol Res Pract, 2011; 207(3); 148-50
9.. Ewell G, Jackson R, Aberrant gastric mucosa in the rectum with ulceration and hemorrhage: Wis Med J, 1939; 38; 641-43
10.. Iacopini F, Gotoda T, Elisei W, Heterotopic gastric mucosa in the anus and rectum: First case report of endoscopic submucosal dissection and systematic review: Gastroenterology Rep (Oxf), 2016; 4(3); 196-205
11.. Mannan AASR, Vieth M, Khararjian A, The outlet patch: Gastric heterotopia of the colorectum and anus: Histopathology, 2018; 73(2); 220-29
12.. Murray FE, Lombard M, Dervan P, Bleeding from multifocal hetero-topic gastric mucosa in the colon controlled by an H2 antagonist: Gut, 1988; 29; 848-51
13.. Ming SC, Simon M, Tandon BN, Gross gastric metaplasia of ileum after regional enteritis: Gastroenterology, 1963; 44(1); 63-68
14.. Ko H, Park SY, Cha EJ, Sohn JS, Colonic adenocarcinoma arising from gastric heterotopia: A case study: Korean J Pathol, 2013; 47(3); 289-92
15.. Breton P, Larget P, Isigor P, [Peptic ulcer of the rectum; Heterotopia of the gastric type (fundique) of the rectal mucosa.]: Arch Mal Appar Dig Mal Nutr, 1955; 44(11); 1153-61 [in French]
16.. Stockman JM, Young VT, Jenkins AL, Duplication of the rectum containing gastric mucosa: JAMA, 1960; 173(11); 1223-25
17.. Srinivasan R, Loewenstine H, Mayle JE, Sessile polypoid gastric heterotopia of rectum: A report of 2 cases and review of the literature: Arch Pathol Lab Med, 1999; 123(3); 222-24
18.. Steele SR, Mullenix PS, Martin MJ, Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the anus: A case report and review of the literature: Am Surg, 2004; 70(8); 715-19
19.. Noguchi T, Takeno S, Takahashi Y, Primary adenocarcinoma of the cervical esophagus arising from heterotopic gastric mucosa: J Gastroenterol, 2001; 36(10); 704-9
20.. Alagozlu H, Ergun M, Cindoruk M, The rare presentations of a large polyp and an esophageal carcinoma in heterotropic gastric mucosa: A case series: J Med Case Rep, 2007; 1; 127
21.. Christensen WN, Sternberg SS, Adenocarcinoma of the upper esophagus arising in ectopic gastric mucosa: Two case reports and review of the literature: Am J Surg Pathol, 1987; 11(5); 397-402
22.. Caruso ML, Marzullo F, Jejunal adenocarcinoma in congenital heterotopic gastric mucosa: J Clin Gastroenterol, 1988; 10(1); 92-94
23.. Schaefer IM, Schüler P, Enders C, High chromosomal instability in adenocarcinoma of the ileum arising from multifocal gastric heterotopia with gastritis cystica profunda: Med Oncol, 2011; 28(4); 1023-26
24.. Vieth M, Kushima R, de Jonge JPA, Adenoma with gastric differentiation (so-called pyloric gland adenoma) in a heterotopic gastric corpus mucosa in the rectum: Virchows Archiv, 2005; 446(5); 542-45
In Press
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943687
17 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943070
17 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943370
18 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943803
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250