11 April 2023: Articles 
A 30-Year-Old Woman with a History of Autoimmune Hyperthyroidism Presenting with Fever and Oral Ulcers, Diagnosed with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Unusual clinical course, Challenging differential diagnosis
Jing Chen1E, Yulei Gao2F*, Yanfen Chai2A, Hua Gao13ADOI: 10.12659/AJCR.938988
Am J Case Rep 2023; 24:e938988
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Lupus erythematosus (LE) is mainly clinically divided into cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) depending on the presence of multi-system manifestations. The most common subtype of CLE is discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Graves’ disease (GD) is immunologically characterized by lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland and the presence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor antibodies (TSH-R-Ab), and is the most common autoimmune pathogenic cause of hyperthyroidism. Autoimmune thyroid dysfunction has been widely described in association with rheumatic diseases. A certain rate of coexistence of GD with LE, mainly SLE, has been reported in the literature. Herein, we present a rare case of Graves’ hyperthyroidism complicated with DLE.
CASE REPORT: A 30-year-old female patient, with a history of hyperthyroidism and discontinued methimazole treatment, initially presented with symptoms of infection and oral ulcers. Thyroid hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibody, and immunological tests were consistent with a diagnosis of Graves’ hyperthyroidism-associated DLE. Corticosteroids and radioactive iodine (RAI) were used to treat DLE and GD, respectively. Post-treatment evaluation suggested the remission of her hyperthyroidism and active DLE.
CONCLUSIONS: Autoimmune thyroid diseases have been previously described in association with rheumatic diseases. This association shows the importance of prompt awareness of the increased risk of DLE when evaluating autoimmune thyroid dysfunction, especially under certain conditions, such as after treatment with anti-thyroid drugs (ATDs), or in the absence of multiple organ damage manifestations of SLE.
Keywords: Graves Disease, Autoimmune Diseases, Lupus Erythematosus, Discoid, Female, Humans, Adult, Oral Ulcer, Iodine Radioisotopes, Thyroid Neoplasms, Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic, hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Diseases, Lupus Erythematosus, Cutaneous, thyrotropin, Rheumatic Diseases
Background
Graves’ disease (GD) is characterized by an increased excitability and metabolism of multiple systems caused by excessive levels of circulating thyroid hormone, such as excitability, palpitations, hyperhidrosis, emaciation, and hyperphagia. The diagnosis of GD is clinically accepted on the basis of biochemical confirmation of thyrotoxicosis, a positive result for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor antibody (TSH-R-Ab) result [1], a hypoechoic and hypervascular thyroid gland on ultrasound, and associated orbitopathy [2]. Lupus erythematosus (LE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that is divided into 2 main clinical types. CLE presents as cellular heterogeneity of lesions that remain localized to the skin or mucosa, and discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) accounts for >80% of such cases [3]. SLE involves manifestations, including cutaneous lupus, polyarthritis, nephritis, seizures, leukopenia, and cognitive impairment [4]. Herein, we report the case of a 30-year-old woman with a history of autoimmune hyperthyroidism who presented with fever, oral ulcers, and some symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection. Appropriate investigations were performed, and the diagnosis of Graves’ hyperthyroidism coexisting with DLE was ultimately established. The relevant literature is discussed regarding the frequency of the coexistence of GD and LE.
Case Report
A 30-year-old woman presented to our hospital with an 8-day history of intermittent fever along with oral ulcers and sore throat, but no cervical pain. With an initial temperature of 37.6°C and a maximum temperature of 39°C, she developed polypnea, sputum production, blurred vision, dyspepsia, anorexia, and diarrhea. On further questioning, the patient confirmed that she had a 1.5-month history of hyperthyroidism, but had lost the medical history, including the results of thyroid hormone tests. After treatment with methimazole (10 mg once daily) and metoprolol (25 mg twice daily) for 5 weeks, the manifestations of lower-limb weakness and tremor improved, but she stopped taking the medication in the last 1 week because of fever. The patient had no other relevant personal medical history, and she also denied a family history of endocrine and autoimmune diseases. On physical examination, her temperature was 37.8°C, heart rate was 118 bpm, blood pressure was 121/62 mmHg, her hands vibrated slightly, and she had a second-degree goiter without tenderness, a swollen tonsil with purulent secretions, and ulcers diffusely distributed over the oral mucosa (Figure 1).
Initial laboratory tests revealed pancytopenia with leukopenia, anaemia, thrombocytopenia with a white blood cell count of 0.63×109/L (reference range 3.50–9.50×109/L), a neutrophil percentage of 3.2% (reference range 40.0–75.0%), and a lymphocyte percentage of 82.5% (reference range 20.0–50.0%), a hemoglobin concentration of 122 g/L (reference range 115–150 g/L), a red blood cell count of 4.73×1012/L (reference range 3.80–5.10×1012/L), and a platelet count of 195×109/L (reference range 125–350×109/L). In addition, her C-reactive protein level was 197.27 mg/L (reference range 0.00–10.00 mg/L), procalcitonin level was 7.74 ng/mL (reference range 0.40–0.50 ng/mL), and erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 58 mm/h (reference range 0–20 mm/h). Laboratory tests showed an elevated values of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase level (84 U/L; reference range 7–49 U/L). Other tests, including urinalysis, coagulation tests, and renal function, were normal. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the head and neck showed significant thickening of the nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal mucosa and enlargement of several cervical lymph nodes, and a gingival biopsy revealed interstitial lymphocytic infiltration of the squamous epithelium (Figure 2). After anti-infective treatment (ceftriaxone for 4 days, piperacillin – sulbactam for 6 days), the patient’s throat swab grew
Laboratory investigations were performed to measure triiodothyronine (T3) (4.92 nmol/L; reference range 0.98–2.33 nmol/L), thyroxine (T4) (158.47 nmol/L; reference range 62.68–150.84 nmol/L), free triiodothyronine (FT3) (5.77 pmol/L; reference range 2.43–6.01 pmol/L), free thyroxine (FT4) (28.65 pmol/L; reference range 9.01–19.05 pmol/L), thyrotropin (<0.004 µIU/ml; reference range 0.350–4.940 µIU/mL), and TSH-R-Ab concentration (33.94 IU/L; reference range 0.00–1.75 IU/L). Thyroid peroxidase antibody was 33.20 IU/mL (reference range 0.00–35.00 IU/mL) and thyroid globulin antibody was <20.0IU/mL (reference range 0.00–40.00 IU/mL). Thyroid ultrasound revealed a diffusely enlarged thyroid gland (left lobe 40.6×27.2×24.2 cm3, right lobe 48.3×28.6×23.7 cm3, anterior and posterior diameter of the isthmus 1.5 cm) with irregular echo and increased blood flow signal. No obvious lobulated glands or pseudo-nodular areas were found. It should be noted that no iodine contrast medium was used in these CT scans involved. In immunological studies, anti-nuclear antibodies detected by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) had a titer of ≥1: 80 (reference range <1: 80).
Her anti-nuclear antibody, anti-Sm antibody, anti-cardiolipin antibody, anti-RNP antibody, anti-nRNP antibody, anti-neutro-phil cytoplasmic antibody C type II, and immunoglobulin M results were all positive, although the anti-DNA antibody or anti-Ro/SSA antibody result was negative. Her C3 and C4 levels decreased to 47.20 mg/dL (reference range 79.00–152 mg/dL) and 4.12 mg/dL (reference range 16.00–38 mg/dL), respectively. The α1-globulin and γ-globulin ratios increased by 9.5% (reference range 53.80–68.20%) and 30.30% (reference range 9.20–18.20%), respectively. Available investigations, including renal function tests, cardiac ultrasound and CT imaging of the chest, abdomen, and head, did not reveal any of the other target organ damage that occurs in lupus patients. Bone marrow biopsy confirmed hyperplasia of the granulocyte series and erythrocyte series, and excluded cytopenia caused by hematological disease.
The diagnosis of Graves’ hyperthyroidism with DLE was made. Basic corticosteroids (starting with 80 mg of methylprednisolone once daily) were used as part of the induced remission therapy for DLE. As for Graves’ hyperthyroidism, considering that DLE may be caused by the use of anti-thyroid drugs (ATDs) with cross-sensitivity, we continued to discontinue methimazole treatment and gave this patient oral compound iodine solution (the initial dose was 6 drops given 3 times daily) with metoprolol (25 mg twice daily) to reduce her heart rate. The patient showed a robust response to recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF), with an increase in neutrophils after 48 hours of application. During the treatment period, her clinical symptoms were rapidly controlled. Relevant laboratory test indicators showed a gradual improvement in abnormal complete blood count values, inflammatory indicators, and liver function test results. Although her TSH level did not fall to the reference range and the TSH-R-Ab result did not turn negative, a reduction in FT3 and FT4 concentrations was observed.
The patient subsequently reduced the dose of methylprednisolone and stopped taking the oral compound iodine solution on the 16th day after treatment, but her FT3 and FT4 were found to be 3 times the upper limit of normal on the 11th day after withdrawal. Thyroidectomy must be performed when the patient’s hyperthyroidism is controlled. As the agranulocytosis had improved significantly and other contraindications had been ruled out, the patient was referred to the Nuclear Medicine Department for treatment with 4 mCi 131I. Without any apparent adverse reaction, the patient was discharged on a therapeutic regime of methylprednisolone (12 mg once daily for 7 days, then 8 mg once daily for 7 days), which was discontinued on day 16 after RAI treatment. A laboratory examination performed 3 months after RAI treatment showed that TSH, FT3, and FT4 concentrations were within the reference ranges, suggesting remission of hyperthyroidism, but the TSHR-Ab result had converted to negative. Considering the long-term incidence of hypothyroidism treated with RAI therapy, it is important to perform follow-up and adjust the treatment plan regularly. Meanwhile, the results of assessment of LE included a SLEDAI score ≤4 points and a Physician Global Assessment (PGA) score ≤1 points with glucocorticoid (GC) ≤7.5 mg; thus, her LE could be considered to exist in a low activity state [5]. The total follow-up time since admission was 4 months and 6 days. Table 1 shows the results of the above indicators at the different evaluation time points. Figure 3 shows the patient’s main medications and the treatment duration.
Discussion
The patient, who met 3 clinical criteria (fever, leukopenia/ thrombocytopenia, and oral ulcers) and 3 immunological criteria (positive anti-cardiolipin antibody, positive anti-dsDNA antibody, low C3, and low C4), had a score of 20 points in the 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for SLE [6]. However, her initial pancytopenia, especially the extreme neutropenia, cannot be considered a specific expression of SLE owing to the comparatively definitive sepsis and severe Graves’ hyperthyroidism.
It is well known that hyperthyroidism can shorten the survival of peripheral blood cells and impair the proliferative potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Meanwhile, the abnormal autoimmunity of patients with GD exacerbates this morbid hematopoiesis [7]. The incidence rate of transient neutropenia, which usually presents as a mild to moderate laboratory abnormality, in patients diagnosed with GD has been reported to be approximately 10% [8]. It is noteworthy that neutrophil counts improve when thyroid hormone levels are reduced, and ATDs are mostly used to alleviate severe pancytopenia in Graves’ hyperthyroidism, despite their dose-dependent adverse effects. It is of great importance to clarify whether this abnormality is due to the disease itself or ATD therapy in order to avoid unnecessary follow-up ATD treatment [9]. However, the basic hematological parameters of our patient were not available before methimazole therapy. We tend to think that the extreme leucopenia in this patient was caused by the thyrotoxic state itself rather than by the ATDs, due to the low dose of the drugs and the rapid improvement of the blood cells.
Because no other target organ damage of SLE was seen apart from the lesion of oral mucosal lesion, her diagnosis of DLE, the most common subtype of CLE, was more appropriate. The predilection for head/neck lesions and the absence of high-titer Ro/SSA antibody on immunodiffusion have been suggested to be effective in differentiating DLE from other less common CLE subtypes, whereas histopathological features do not appear to be definitive [10]. Oral discoid lesions, which are most widely distributed in labial and buccal mucosa, may occur without or before skin lesions. Severe neutropenia is associated with oral ulcers, reflecting disease activity and susceptibility to infection [11]; thus, the oral ulcer of our patient was more likely a manifestation of DLE and granulocytopenia.
As a result of the loss of immunological tolerance to self-antigens, autoimmune diseases encompass a broad spectrum of disorders that can manifest as organ-specific or systemic, which can overlap with each other. The literature to date has reported many cases of autoimmune thyroid dysfunction and SLE coexisting worldwide, whereas few cases of patients with concurrent GD and DLE have been reported. The present case describes a possible association between auto-immune hyperthyroidism and DLE. On the one hand, definite cases in which autoimmune thyroid dysfunction appeared to be more frequent in SLE patients than the general population [12,13]. SLE patients, with or without clinical evidence of functional thyroid dysfunction, are prone to produce elevated circulating anti-thyroglobulin antibodies, anti-thyroid antibodies, and anti-thyroid microsomal antibodies, high titers of which may help to predict the possible presence of autoimmune thyroid disease [14]. On the other hand, research shows that GD is associated with a higher positive rate of incident SLE. Hyperthyroidism accelerates the basal metabolism and increases oxygen consumption and the production of reactive oxygen radicals, increasing oxidative stress leads to tissue peroxidation in the antioxidant defense system, and the immunological responses correlate with the disease activity and organ damage of SLE [15–17]. The role of cytokines and chemokines may be responsible for the inflammatory organ-damaging response [18]. The amplification feedback loop created by T helper 1 (Th1) lymphocytes and IFN-γ-inducible protein 10 (IP-10/CXCL10) initiates and perpetuates the thyroid autoimmune and destruction process of GD. CXCL10 also contributes to the pathogenesis of LE by binding to the C-X-C motif receptor 3 (CXCR3) [19].
LE is a systemic disease associated with innate and adaptive autoimmune responses, leading to a loss of self-tolerance [20]. A possible role of infection in triggering or exacerbating LE could be hypothesized in this case. The serious but relatively minor side effects of ATD-induced lupus erythematosus-like syndrome may be related to the interaction of drugs with nuclear antigens and lymphocytes, immunoglobulin A deficiency, and the genetic basis indicated by the HLA type associated with SLE in predisposed individuals [21]. Although definitive criteria have not been established, improvements in clinical symptoms and reductions in auto-antibody titers after withdrawal of ATDs are conducive to distinguishing idiopathic lupus erythematosus from drug-induced lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. The onset time of SLE was unclear due to the patient’s lack of a relevant immunological index before the diagnosis of GD. The associated clinical manifestations were relieved after discontinuation of the drug, and the possibility of ATD-induced lupus erythematosus cannot be excluded.
Conclusions
With some shared pathogenic mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, the association between autoimmune thyroid disease and SLE has been widely reported. The present case shows that clinicians need to be aware of the possible but relatively rare coexistence of Graves’ hyperthyroidism and DLE. In such a complicated situation, patients’ clinical features, such as fever, ulcers, and leukopenia, can be manifestations of multiple factors, including Graves’ hyperthyroidism, side effects of ATDs, abnormal autoimmunity attributed to LE, and severe infection.
Figures
References:
1.. Rasaei N, Shams M, Kamali-Sarvestani E, Nazarinia MA, The prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Iran Red Crescent Med J, 2015; 17(12); e17298
2.. Kahaly GJ, Bartalena L, Hegedus L, 2018 European Thyroid Association guideline for the management of Graves’ hyperthyroidism: Eur Thyroid J, 2018; 7(4); 167-86
3.. Zheng M, Hu Z, Mei X, Single-cell sequencing shows cellular heterogeneity of cutaneous lesions in lupus erythematosus: Nat Commun, 2022; 13(1); 7489
4.. Tsokos GC, Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: Nat Immunol, 2020; 21(6); 605-14
5.. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A, 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: Ann Rheum Dis, 2019; 78(6); 736-45
6.. Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus: Ann Rheum Dis, 2019; 78(9); 1151-59
7.. Scappaticcio L, Bellastella G, Maiorino MI: Graves’ hyperthyroidism-related pancytopenia: A case report with literature review: Hormones (Athens), 2021; 20(1); 93-100
8.. Scappaticcio L, Maiorino MI, Maio A, Neutropenia in patients with hyperthyroidism: Systematic review and meta-analysis: Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2021; 94(3); 473-83
9.. Aggarwal N, Tee SA, Saqib W, Treatment of hyperthyroidism with antithyroid drugs corrects mild neutropenia in Graves’ disease: Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2016; 85(6); 949-53
10.. Haber JS, Merola JF, Werth VP, Classifying discoid lupus erythematosus: Background, gaps, and difficulties: Int J Womens Dermatol, 2016; 2(1); 8-12
11.. Meyer A, Guffroy A, Blaison G, Systemic lupus erythematosus and neutropaenia: A hallmark of haematological manifestations: Lupus Sci Med, 2020; 7(1); e000399
12.. Ferrari SM, Elia G, Virili C, Systemic lupus erythematosus and thyroid autoimmunity: Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2017; 8; 138
13.. Lin WY, Chang CL, Fu LS, Systemic lupus erythematosus and thyroid disease: A 10-year study: J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2015; 48(6); 676-83
14.. Posselt RT, Coelho VN, Skare TL, Hashimoto thyroiditis, anti-thyroid antibodies and systemic lupus erythematosus: Int J Rheum Dis, 2018; 21(1); 186-93
15.. Lozovoy MA, Simao AN, Panis C, Oxidative stress is associated with liver damage, inflammatory status, and corticosteroid therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Lupus, 2011; 20(12); 1250-59
16.. Agan V, Celik H, Eren MA, An investigation of oxidative stress and thiol/disulphide homeostasis in Graves’ disease: Medicina (Kaunas), 2019; 55(6); 275
17.. Lee C, Chen SF, Yang YC, Association between Graves’ disease and risk of incident systemic lupus erythematosus: A nationwide populationbased cohort study: Int J Rheum Dis, 2021; 24(2); 240-45
18.. Tsokos GC, Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: Nat Immunol, 2020; 21(6); 605-14
19.. Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Corrado A, Autoimmune thyroid disorders: Autoimmun Rev, 2015; 14(2); 174-80
20.. Szyper-Kravitz M, Marai I, Shoenfeld Y, Coexistence of thyroid autoimmunity with other autoimmune diseases: Friend or foe? Additional aspects on the mosaic of autoimmunity: Autoimmunity, 2005; 38(3); 247-55
21.. Sato-Matsumura KC, Koizumi H, Matsumura T, Lupus erythematosus-like syndrome induced by thiamazole and propylthiouracil: J Dermatol, 1994; 21(7); 501-7
Figures
Tables
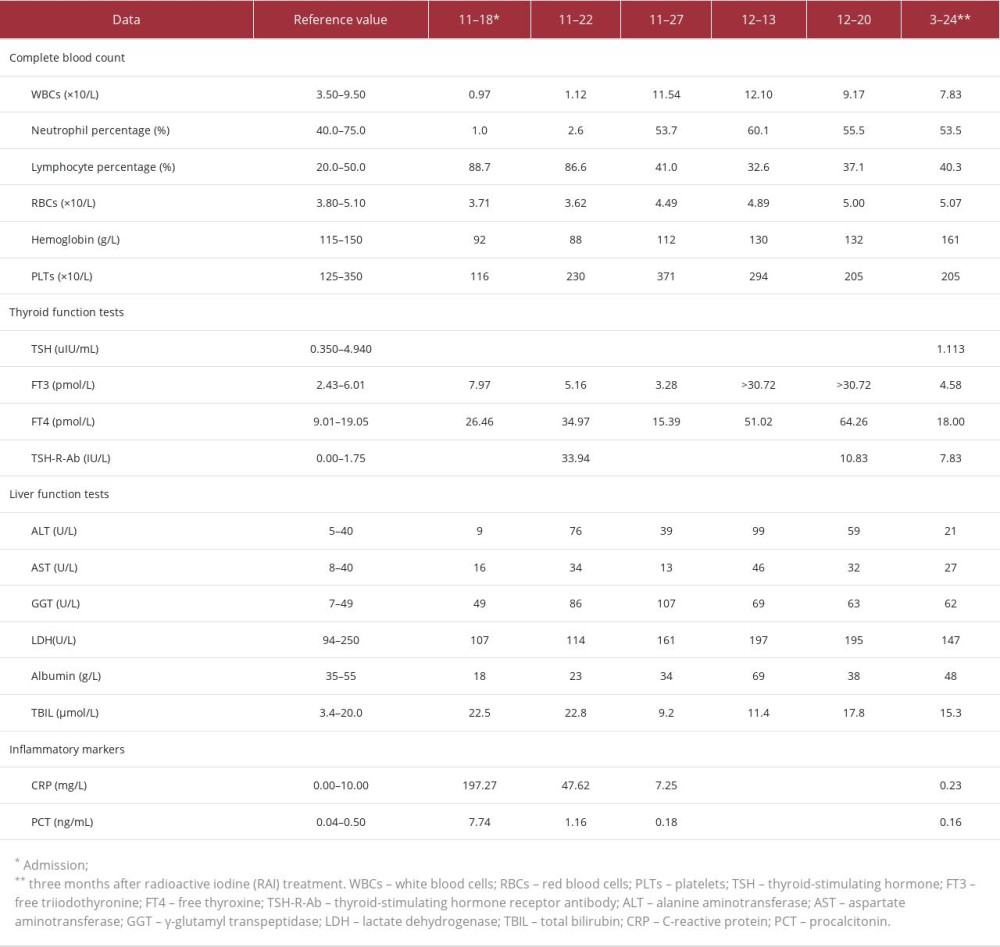 Table 1.. Results of complete blood count, thyroid function tests, TSH-R-Ab, liver function tests, and inflammatory markers at the different evaluation points.
Table 1.. Results of complete blood count, thyroid function tests, TSH-R-Ab, liver function tests, and inflammatory markers at the different evaluation points. Table 1.. Results of complete blood count, thyroid function tests, TSH-R-Ab, liver function tests, and inflammatory markers at the different evaluation points.
Table 1.. Results of complete blood count, thyroid function tests, TSH-R-Ab, liver function tests, and inflammatory markers at the different evaluation points. In Press
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942770
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943214
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943010
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943687
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250








