18 December 2023: Articles 
Successful Treatment of Fishbone-Induced Esophageal Perforation and Mediastinal Abscess: A Case Report and Literature Review
Unusual or unexpected effect of treatment, Rare disease
Shili Zhong1ABCE, Zhengbin Wu1AE*, Zheng Wang1CEDOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942056
Am J Case Rep 2023; 24:e942056
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Fish bone ingestion is the most common cause of esophageal perforation (12%). However, it rarely causes esophageal perforation and mediastinal abscess. Most studies recommend surgical intervention for patients with esophageal perforation and thoracic abscess. However, surgery may not be suitable for extremely critical cases or may have limited effectiveness. In such cases, a combination of surgery and conservative treatment is crucial. The use of double cannula irrigation and drainage in conservative treatment has shown promising results in pus removal.
CASE REPORT: We report a 28-year-old man with a perforated esophagus with abscess and mediastinal abscess due to fish bone. Emergency surgery was performed after admission. Symptoms of septic shock developed after surgery, and a significant amount of pus was still present in the chest cavity and mediastinum. Conservative treatment was adopted, with double cannula irrigation and drainage. By employing anti-infection measures and continuous irrigation and drainage, the patient was cured after 42 days.
CONCLUSIONS: In this case, surgical intervention did not yield satisfactory results. However, after using double cannula irrigation and drainage to clear the thoracic and mediastinal abscesses, the patient’s infection levels returned to normal. Additionally, the patient was successfully weaned off the ventilator, and the tracheotomy catheter was removed. After discharge, the patient resumed to normal life, without any significant complications during 1 year of follow-up. Double cannula drainage played a vital role in this patient’s treatment; however, further clinical evidence is required to determine its suitability for other patients with esophageal perforation complicated by mediastinal abscess.
Keywords: Esophageal Perforation, Debridement, Drainage, Mediastinal Diseases
Background
Esophageal perforation is primarily caused by iatrogenic factors, such as endoscopic examination and treatment, which account for 59% of cases [1]. Exogenous trauma rarely leads to esophageal perforation. Among exogenous foreign bodies, fish bones are the most common cause (12%) [2]. However, simultaneous occurrence of esophageal perforation and mediastinal abscess is rare. Patients with complications such as thoracic abscess, mediastinal abscess, sepsis, and septic shock have a mortality rate of up to 66% [1,2]. Early identification and diagnosis are crucial for managing esophageal perforation. Research indicates that the mortality rate increases as the duration of perforation is prolonged. Currently, surgical treatment or simple drainage is used to manage esophageal perforation complicated with mediastinal abscess. However, thoracoscopic surgery presents challenges owing to the presence of fibrin or pus cavity separation, which hinder clear tissue structure distinction under the microscope and can result in incomplete abscess drainage. In this article, we present a successful case from our department in 2022 involving esophageal perforation caused by a fish bone in conjunction with mediastinal abscess and empyema. The purpose of this article is to share and discuss the treatment methods used.
Case Report
The patient was a 28-year-old man who experienced a foreign body sensation in the throat 8 days before admission due to sticking his throat while eating fish. The foreign body sensation worsened during swallowing, and the patient improved after drinking more water on his own. Seven days before admission, the patient developed a fever with a maximum temperature of 39°C. The patient went to the hospital for gastroscopy, and no obvious abnormalities were found. One day before admission, the patient felt that chest tightness had worsened and repeatedly experienced high fever. Physical examination was conducted immediately after the patient entered the Emergency Department. The body temperature was 40°C. The patient’s lips were slightly purple, and he had shortness of breath. The respiratory rate was 25 breaths/min. Physical examination and auscultation found that the right side of the respiratory tract was reduced, and the right side of the spoken voice was reduced. Emergency blood gas analysis showed the oxygenation index was only 83 mmHg. Within half an hour after admission, the patient underwent emergency contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the chest, which showed the following: the right wall of the upper esophageal segment (approximately at the level of the chest’s second vertebral body) appeared discontinuous, with cystic low-density shadows around it; liquid plane formation was observed inside, with a larger section of about 8.5×5.6 cm; circular low density shadow could be seen in the right chest cavity, with a liquid plane formation inside, and a larger layer of approximately 11.2×7.1 cm; right pleural effusion was partially enveloped; and there was right lung partially compressed atelectasis, excluding esophageal perforation and abscess formation (Figure 1A–1C). Laboratory auxiliary examination results showed blood routine white blood cell count of 28.42×109/L, total number of neutrophils of 20.99×109/L, platelet count of 70×109/L, whole blood high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level of 198.51 mg/L, procalcitonin level over 100 ng/mL, and interleukin-6 level over 5000 pg/mL. Liver function test results showed albumin of 21 g/L, glutamic acid transaminase of 780 u/L, and total bilirubin of 140 umol/L. Renal function test results showed blood creatinine of 250.1 umol/L and urea nitrogen of 15 umol/L.
After further examination, the diagnoses were esophageal perforation, empyema, mediastinal abscess, sepsis, septic shock, acute respiratory distress syndrome (severe), and type I respiratory failure. The Emergency Department team immediately had a joint consultation with a critical care physician, thoracic surgeon, and gastroenterologist to consider the patient’s esophageal perforation, empyema, and mediastinal abscess. The APACHE II score was 21 points, risk factor of death was 75.2%, and SOFA score (sequential organ failure score) was 14 points. After discussion, emergency thoracoscopic right chest exploration was planned. Before the operation, the patient was given imipenem for wide coverage anti-infection. During the operation, a large amount of dense adhesions and fiber wrapping were observed in the chest cavity, as well as a large amount of yellow-brown pus. The lungs showed a large amount of yellow-white pus coating, which was difficult to operate under the microscope. Therefore, the surgical method was changed from thoracoscopic to thoracotomy. During the operation, significant thickening and edema of the mediastinum pleura at the azygos vein arch was observed. There was a large amount of yellow-brown pus in the mediastinal pleura, but after detailed exploration, no obvious esophageal perfo-ration sign was found, and no residual fish bone foreign body was found. A gastric tube was placed 20 cm away from the incisor teeth. After the injection of a diluted solution of methylene blue through a gastric tube, the surrounding tissues of the esophagus were carefully explored, and no blue solution was found to have escaped. Subsequently, the patient’s empyema was cleared, pleural fiberboard was stripped, and mediastinal drainage was performed.
After the surgery, the patient was transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). The patient’s heart rate fluctuated between 130 to 150 beats/min, breathing was 50 breaths/min, which was assisted by a ventilator (SIMV+PSV mode, FiO2 100%). The oxygenation index was 88 mmHg, and norepinephrine 0.6 to 0.8 ug/kg/min was given to maintain the blood pressure around 120/55 mmHg. The patient’s blood lactate level increased from 5.5 to 8.0 mmol/L, indicating sepsis and septic shock. Gram-positive cocci and gram-negative bacilli could be seen in the pus smear of the patient during the operation. The patient was given imipenem and tigecycline for anti-infection. At the same time, the patient was given continuous renal replacement treatment with the mode of continuous veno-venous hemofiltration and hemoperfusion to remove inflammatory mediators and stabilize circulation.
One week after being transferred to the ICU, the patient still had recurrent fever, with a maximum temperature of 41°C. Antibiotic treatment was not effective. The patient’s contrast-enhanced chest CT showed that there was still pus accumulation in the patient’s chest and mediastinum, and no perforation was found after completing the gastroscopy examination. The patient’s chest was punctured and drained, and yellow pus was extracted. The pus culture results showed drug-resistant
The third week after being transferred to the ICU the patient still had intermittent fever, with a highest temperature of 39.5°C, and shock symptoms such as decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate, and increased respiratory rate had occurred. After 1 day of anti-shock treatment, the patient improved. He underwent enhanced chest CT examination again, and it could be seen that the patient’s pleural pus had decreased, compared with before. The right lower lung had become severely consolidated, and there was still a large amount of pus in the mediastinum. The patient was again placed with double drainage tubes through mediastinal puncture, the 2 double tubes were washed with 1000 mL isodialysis solution every 2 to 3 h, and a large number of yellow and white suppurating strips were drained (Table 1, Figure 3). At the same time, the patient was given ventilation treatment in the prone position and gradually improved. Re-examination of the infection index showed routine white blood cell count of 10.8×109/L, total number of neutrophils of 7.5×109/L, platelet count of 141×109/L, whole blood high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level of 18 mg/L, procalcitonin over 0.27 ng/mL, and interleukin-6 over 16 pg/mL. It was arranged for the patient to get out of bed for rehabilitation training, and ultimately he successfully recovered after 7 weeks of treatment (Figure 1D, 1E). The patient was able to live normally and reported no special discomfort during a continuous follow-up period of 1 year.
Discussion
The management of esophageal perforation continues to be a significant challenge. Currently, the mortality rate of esophageal perforation is 33%. Severe complications, such as mediastinal abscess or artery rupture, can double the mortality rate, and delayed diagnosis also increases the risk [1,2]. Recent literature reports indicate that esophageal perforation caused by fish bone typically occurs in the 3 physiological strictures of the esophagus [2,3]. Diagnosing esophageal perforation can be difficult since atypical symptoms, such as pharyngeal discomfort, are present in one-third of cases, leading to delayed diagnosis and increased mortality rates [2]. Table 2 shows the review of 4 articles on perforation of esophagus caused by fish bones in the past 10 years. It is worth noting that 1 case in 2019 remained undiagnosed for 3 days, resulting in the patient’s death, while the remaining 3 cases, including the present case, were all diagnosed within 24 h. Felmly et al found that as the time from perforation to treatment increases, the opportunity for successful initial repair decreases, the need for stents and drainage increases, and the mortality rate rises [3]. Various diagnostic methods, such as chest X-ray, esophagography, CT scans, gastroscopy, and laryngoscopy, can be used to diagnose esophageal perforation. However, even in cases in which these examinations yield negative results but clinical symptoms persist, esophageal perforation remains highly suspected. This patient experienced discomfort in the throat immediately after the onset of symptoms, and both gastroscopy and chest CT examinations came back negative. After multidisciplinary discussions, esophageal perforation was still considered as a possibility. Due to the loose tissue structure surrounding the esophagus, bacteria and gastric juice can easily reach the mediastinum, leading to abscess formation and potential complications such as sepsis and multiple organ failure. Early identification and timely treatment are crucial to reducing the high mortality rate associated with esophageal perforation [4,5].
Based on the patient’s clinical symptoms, physical examination, imaging, and laboratory indicators, the presence of esophageal perforation, empyema, and mediastinal abscess was considered. Multidisciplinary discussions were immediately initiated, leading to surgical treatment for the patient. During the surgery, pus smear and culture were conducted to identify the responsible pathogens. After the surgery, the patient was transferred to the ICU for further support and treatment.
The choice of treatment methods for esophageal perforation depends on several factors, including the cause, location, and size of the perforation, the time interval between perforation and diagnosis, potential esophageal diseases of the patient, and overall health status of the patient [6,7]. Small perforations can be sealed through methods such as fibrin glue injection and metal stents, with minimal sequelae. However, in some cases, even with methods like methylene blue injection, it may not be possible to locate the perforation site accurately. Non-surgical treatments, such as adequate local drainage, can be effective for patients with intrathoracic esophageal perforation limited to the mediastinum [8,9]. However, if the perforation is not limited to the mediastinum, if there are multiple pus cavities, signs of shock, or if the perforation affects nearby structures like the pleura, pericardium, or peritoneum, prompt surgical intervention is necessary [10]. Table 2 [11–14] indicates that patients with esophageal perforation complicated with mediastinal abscess can benefit from both surgery and conservative drainage. In some cases, additional treatment, such as endoscopic protein glue, can be required to treat complications, like esophageal fistula. In this case, the patient presented with multiple pus cavities and septic shock, requiring thoracoscopic exploration and debridement to save his life. Early diagnosis and treatment, in combination with multidisciplinary discussions, are crucial in managing esophageal perforation effectively.
In clinical practice, it has been found that surgical treatment is often necessary for most patients with esophageal perforation, especially those with clear leaks. However, thoracotomy can be traumatic and may not be suitable for some critically ill patients. Fortunately, clinical evidence has shown that fibrin glue injection is an effective method for sealing leaks. By promoting the closure of the fistula and the growth of granulation tissue around it, fibrin glue offers a noninvasive alternative to surgery, and local drainage can facilitate healing [9,10]. In the present case, the patient did not exhibit a clear fistula following surgical treatment. However, enhanced chest CT examination revealed the presence of pyothorax and mediastinal pus. Due to the thick consistency of the pus, surgical debridement and drainage were not feasible. Instead, the patient’s condition required repeated rinsing with physiological saline, intermittent pus collection for cultivation, and observation of pus characteristics. To address these challenges, the decision was made to use double cannula irrigation and drainage. This approach offers 2 advantages: First, negative pressure suction helps remove pus from the cavity, reducing bacterial count, alleviating local inflammation, and promoting wound healing; and second, sealing the front end of the outer tube prevents damage to chest and mediastinum tissues, while the inner tube allows for sufficient flushing and drainage. With extensive experience in double cannula irrigation and drainage in areas such as the chest and abdominal cavity, our department performed this procedure for the mediastinum for the first time. As a result, yellow and white fibrous purulent strips were drained after irrigating the patient’s mediastinum with physiological saline. The patient’s fever significantly improved compared with before. By continuing double cannula irrigation, enhancing nutritional support and incorporating rehabilitation exercise, the patient successfully recovered. This case exemplifies the importance of combining debridement surgery with conservative double cannula irrigation for esophageal perforation treatment.
Conclusions
In this case, surgical intervention did not yield satisfactory results. However, after using double cannula irrigation and drainage to clear the thoracic and mediastinal abscesses, the patient’s infection levels returned to normal. Meanwhile, the patient was successfully weaned off the ventilator and the tracheotomy catheter was removed. Following discharge, the patient resumed normal life, without any significant complications during 1 year of continuous follow-up. Double cannula drainage played a critical role in the treatment of this patient; however, further clinical evidence is required to determine its suitability for other patients with esophageal perforation complicated by mediastinal abscess.
Figures
References:
1.. Brinster CJ, Singhal S, Lee L, Evolving options in the management of esophageal perforation: Ann of Thorac Surg, 2004; 77(4); 1475-83
2.. Bufkin BL, Miller JI, Mansour KA, Esophageal perforation: Emphasis on management: Ann of Thorac Surg, 1996; 61(5); 1447
3.. Felmly LM, Kwon H, Denlinger CE, Klapper JA, Esophageal perforation: A common clinical problem with many different management options: Am Surg, 2017; 83(8); 911-17
4.. Shibuya H, Ikehara H, Andoh K, Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of a mediastinal abscess caused by an ingested fish bone: Intern Med, 2019; 58(15); 2173-77
5.. Joshi AA, Bradoo RA, A foreign body in the pharynx migrating through the internal jugular vein: Am J Otolaryng, 2003; 24(2); 89-91
6.. Peng A, Li Y, Xiao Z, Study of clinical treatment of esophageal foreign body-induced esophageal perforation with lethal complications: Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-L, 2012; 269(9); 2027-36
7.. Leo MD, Maselli R, Ferrara EC, Endoscopic management of benign esophageal ruptures and leaks: Curr Opin Gastroen, 2017; 15(2); 1-17
8.. Tsalis K, Blouhos K, Kapetanos D, Conservative management for an esophageal perforation in a patient presented with delayed diagnosis: A case report review of the literature: Cases J, 2009; 2; 6784
9.. Freeman RK, Herrera A, Ascioti AJ, A propensity-matched comparison of cost and outcomes after esophageal stent placement or primary surgical repair for iatrogenic esophageal perforation: J Thorac Cardiov Surg, 2015; 149(6); 1550-55
10.. Huang TT, Tseng FY, Yeh TH, Factors affecting the bacteriology of deep neck infection: a retrospective study of 128 patients: Acta Oto Laryngol, 2006; 126(4); 396-401
11.. Lambert RG, Angmorterh SK, Benjamin MB, Esophageal perforation by tilapia fish bone ingestion – a case report: Int J Surg Case Rep, 2020; 71; 23-26
12.. Zhao S, Tinzin L, Deng W, Sudden unexpected death due to left subclavian artery-esophageal fistula caused by fish bone: J Forebsic Sci, 2019; 64(6); 1926-28
13.. Wang J, Wu WB, Chen L, Video-mediastinoscopy assisted fish bone extraction and superior Medistinal abscess debridement: J Cardiothorac Sugr, 2018; 13(1); 38
14.. Kimura T, Takemoto T, Fujiwara Y, Esophageal perforation caused by a fish bone treated with surgically indwelling drainage and fibrin glue injection for fistula formation: Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2013; 19(4); 289-92
Figures
Tables
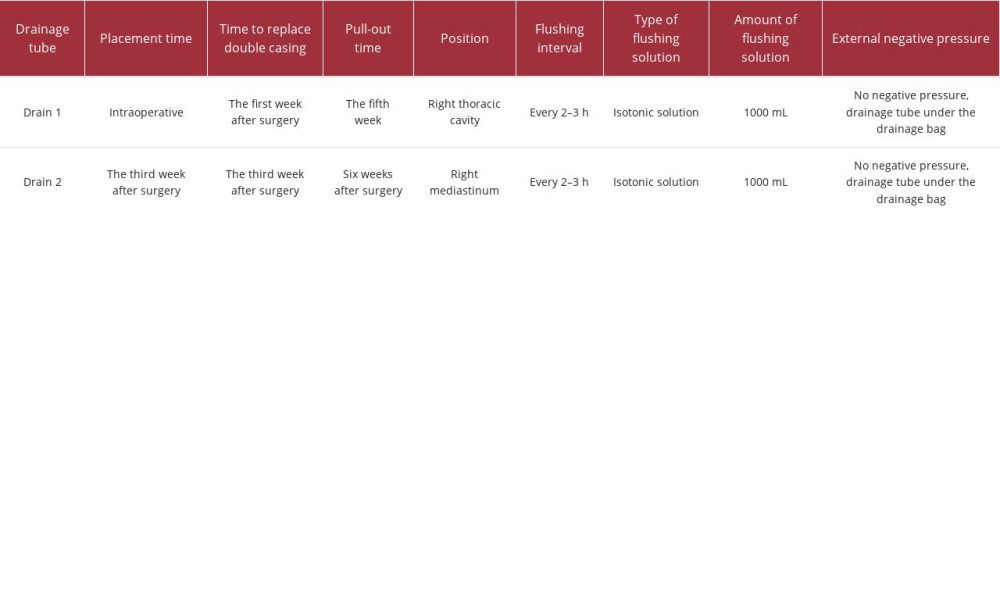 Table 1.. The irrigation schedule of the double cannula.
Table 1.. The irrigation schedule of the double cannula.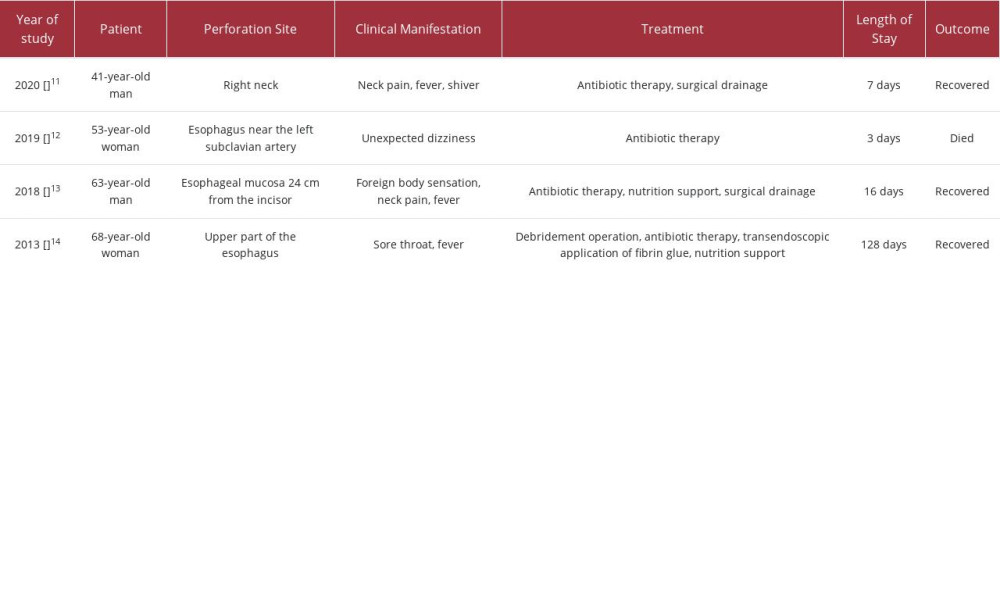 Table 2.. Clinical characteristics of esophageal perforation caused by fish bone in 2013, 2018, 2019, and 2020.
Table 2.. Clinical characteristics of esophageal perforation caused by fish bone in 2013, 2018, 2019, and 2020. Table 1.. The irrigation schedule of the double cannula.
Table 1.. The irrigation schedule of the double cannula. Table 2.. Clinical characteristics of esophageal perforation caused by fish bone in 2013, 2018, 2019, and 2020.
Table 2.. Clinical characteristics of esophageal perforation caused by fish bone in 2013, 2018, 2019, and 2020. In Press
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942853
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942660
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943174
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943136
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250








