02 April 2024: Articles 
Hemorrhagic Presentation in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Case Study
Unusual clinical course, Challenging differential diagnosis
Filipa Marques Rodrigues1ABCDEF*, Mariana Santos2BCDF, Ricardo Martins2DFDOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942951
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e942951
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an extremely aggressive brain disease that rarely affects immunocompetent non-elderly patients, particularly with hemorrhagic presentation. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays an important role in the diagnosis of this entity, which typically demonstrates restricted diffusion and a T2 hypointense appearance, suggesting hypercellularity.
CASE REPORT: A 44-year-old man came to the emergency department with a persistent and treatment-resistant bilateral frontal headache that had been bothering him for the past 3 weeks. Upon conducting a neurological assessment, the patient displayed temporal disorientation and incoherent speech, but without any observable motor deficits. A non-contrast enhanced brain computed tomography scan was carried out, revealing a hyperattenuating, space-occupying lesion and hemorrhage in the left hemisphere of the brain. Subsequently, brain MRI demonstrated hypointense signal on T2-weighted images, restricted diffusion, and homogeneous lesional contrast enhancement, suggesting a very cellular expansive lesion with hemorrhage. To establish a definitive diagnosis, a brain biopsy was undertaken, confirming the presence of DLBCL of the primary central nervous system (germinal center phenotype).
CONCLUSIONS: Hemorrhagic presentation of primary central nervous system DLBCL occurs very rarely, particularly in non-elderly immunocompetent patients. Brain MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis of this entity, which allows differentiation from high-grade glial or other lesions that present more frequently with hemorrhage. Therefore, it is crucial to suspect lymphoma before surgical intervention for appropriate patient management.
Keywords: Intracranial Hemorrhages, Lymphoma, B-Cell, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Introduction
Primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of brain lymphoma, accounting for 80–85% of cases [1]. There is a male predominance and most are diagnosed over the age of 50 years. The most typical presentation is a solitary mass with predilection for the periventricular region. Primary central nervous system DLBCL in immunocompetent patients usually has homogeneous appearance, without necrotic areas or hemorrhage [2]. Theoretically, the presence of hemorrhage or areas of necrosis on imaging in immunocompetent patients is considered to disfavor a diagnosis of lymphoma [3]. Hemorrhage is very rarely observed in untreated central nervous system lymphoma. However, it could be potentially explained by high immunore-activity to vascular endothelial growth factor and tumor invasion, leading to the breakdown of the vessel wall.
The present study aims to delve into the intricacies of primary central nervous system DLBCL with a focus on the infrequent yet significant occurrence of hemorrhagic complications. By examining the complexities associated with diagnosis and management, particularly in cases where infiltrative/expansive lesions exhibit a hemorrhagic component, our objective is to contribute insights that enhance awareness and understanding within the medical community.
Case Report
A 44-year-old man with a history of psoriasis, who, at the time, was not taking his prescribed medication, presented to the emergency department with a 3-week history of bilateral frontal headache that did not improve with analgesic treatment. The patient denied other symptoms, such as weight loss, nausea, or vomiting. Neurological examination revealed temporal disorientation and confused speech without motor deficits. The blood test was unremarkable, especially in relation to inflammatory parameters.
A non-contrast enhanced brain computed tomography (CT) exam showed a hyperattenuating, space-occupying lesion and hemorrhage in the left hemisphere (Figure 1). Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Figure 2) was performed 8 days later for further evaluation, demonstrating hypointense signal on T2-weighted images, restricted diffusion, and homogeneous lesional contrast enhancement. A late subacute hemorrhage was found next to this area. On perfusion study, low relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) values were revealed, favoring the hypothesis of a lymphoproliferative tumor over a high-grade glial tumor. These findings were suggestive of a hemorrhagic brain lymphoma. One week later, brain biopsy was performed and the diagnosis of DLBCL of the primary central nervous system (germinal center phenotype) was confirmed 8 days afterwards. Immunohistochemistry examination was positive for CD20, bcl6, and bcl2.
Chemotherapy and supportive care were started 1 month after the diagnosis; however, progressive clinical deterioration was noted and the patient died 4 months after the diagnosis.
Discussion
Primary central nervous system DLBCL is a highly malignant brain disease and the germinal center subtype is rare [4]. Although this subtype is considered rare, the literature reports better clinical outcomes compared with non-germinal center subtype [5]. The disease in immunocompetent patients typically presents as a solitary lesion with predilection for the periventricular white matter, with possible involvement of the gray matter [6]. Brain MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis of this entity, which is characterized by restricted diffusion and T2 hypointense signal, suggesting hypercellularity [7]. On per-fusion study, these lesions show lower rCBV compared with high-grade glioma, supporting this differential diagnosis [7,8].
Surprisingly, this patient presented with a hemorrhagic complication of DLBCL, which is a rare feature in immunocompetent patients [9,10]. Primary brain lymphoma is usually confined to the parenchyma and rarely invades blood vessels.
Additionally, angiogenesis occurs in brain lymphomas, but it is not as harmful to the blood vessels as it may be in some other types of brain tumors, such as in gliomas [11]. Some of these factors may explain the lower frequency of bleeding in brain lymphoma; however, it is important to note that while bleeding is not a typical feature of primary brain lymphoma, the symptoms and complications associated with the tumor can still be severe and require medical attention.
Immunocompromised patients, including those with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, may be more susceptible to certain complications, including intra-tumoral bleeding in a primary central nervous system lymphoma. Infection of the central nervous system can cause inflammation and blood vessel damage, potentially leading to bleeding. Additionally, weakened immune responses can contribute to vascular fragility, making blood vessels more prone to damage and bleeding [12].
In fact, the presence of hemorrhage per se could have suggested the diagnosis of other brain tumors, such as high-grade gliomas [10]. However, hyperdensity on CT, low T2 signal, diffusion restriction, homogeneous contrast enhancement, and low rCBV were noted on MRI. These are essential features to favor the diagnosis of central nervous system lymphoma.
The present study has some limitations, as with any single-case report: the findings may not be broadly generalizable to all cases of primary central nervous system DLBCL, and reliance on retrospective data may potentially limit the ability to establish causal relationships or temporal sequences. The authors suggest that conducting larger, prospective studies could further elucidate the incidence and clinical characteristics of hemorrhagic presentations in primary central nervous system DLBCL. Additionally, investigating optimal treatment strategies for cases presenting with hemorrhage may guide more effective management of this atypical manifestation. Follow-up studies exploring the long-term outcomes and disease progression in patients with similar presentations can contribute to a better understanding of the prognosis and management challenges associated with this specific subtype.
Conclusions
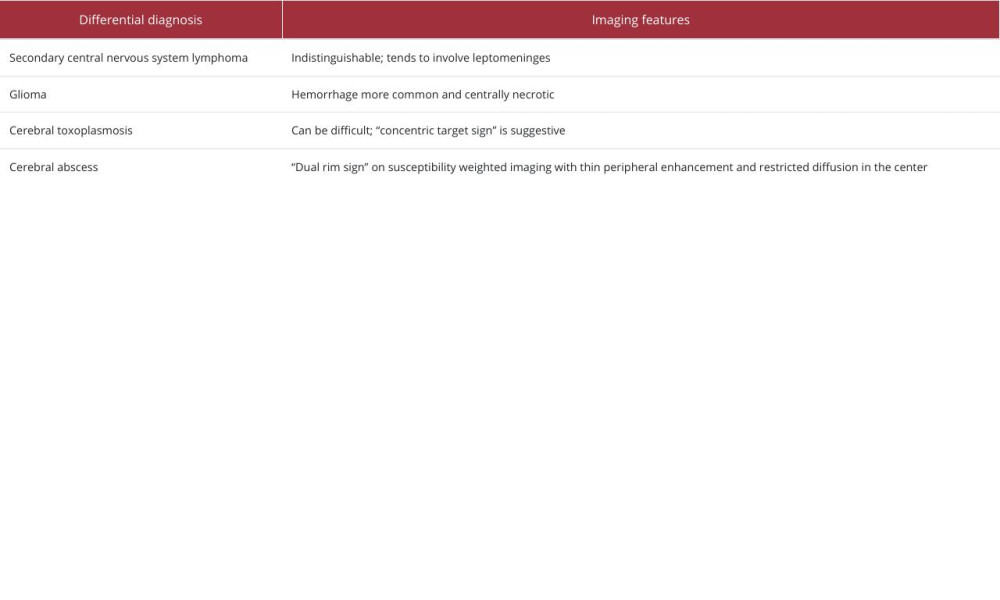
To our knowledge, there are few cases described in the literature reporting this type of manifestation of a primary central nervous system lymphoma in an immunocompetent non-elderly patient. Brain MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis of this entity, which has characteristic features, such as hypointense signal on T2-weighted images, restricted diffusion, and hypoperfusion, helping to differentiate it from high-grade glial tumors, which are most often associated with intralesional hemorrhage. In this case, the location of the lesion may have contributed to the hemorrhage due to the proximity of perforating arteries, potentially due to vascular wall fragility. Therefore, in a patient with an infiltrative/expansive lesion with a hemorrhagic component, advanced MRI techniques must be undertaken to help in the differential diagnosis (Table 1).
Every individual case is unique, and the specific characteristics of a tumor can vary. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with suspected brain tumors to undergo a thorough diagnostic evaluation by healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Figures
References:
1.. Pons-Escoda A, Naval-Baudin P, Velasco R, Vidal N, Majós C, Imaging of lymphomas involving the CNS: An update-review of the full spectrum of disease with an emphasis on the World Health Organization Classifications of CNS Tumors 2021 and Hematolymphoid Tumors 2022: Am J Neuroradiol, 2023; 44(4); 358-66
2.. Haldorsen I, Kråkenes J, Krossnes B, CT and MR imaging features of primary central nervous system lymphoma in Norway: Am J Neuroradiol, 2009; 30(4); 744-51
3.. Jhaveri MD, Osborn AG, Salzman KL, Jhaveri MD, Chapter 173: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Diagnostic imaging: Brain, 2020; 602-6, Philadelphia, PA, Elsevier
4.. Visco C, Tzankov A, Xu-Monette ZY, Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of germinal center origin with BCL2 translocations have poor outcome, irrespective of MYC status: a report from an International DLBCL rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study: Haematologica, 2013; 98(2); 255-63
5.. Marcus C, Maragkos GA, Alterman RL, Uhlmann E, Pihan G, Varma H, GCB-type is a favorable prognostic factor in primary CNS diffuse large B-cell lymphomas: J Clin Neurosci, 2020; 83; 49-55
6.. Plasswilm L, Herrlinger U, Korfel A, Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: Ann Hematol, 2002; 81; 415-23
7.. Kwok HM, Li KY, Chan RLS, Different facets of intracranial central nervous system lymphoma and its imaging mimics: J Clin Imaging Sci, 2022; 12; 4
8.. Suh CH, Kim HS, Jung SC, MRI as a diagnostic biomarker for differentiating primary central nervous system lymphoma from glioblastoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis: J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019; 50; 560-72
9.. Blasel S, Vorwerk R, Kiyose M, New MR perfusion features in primary central nervous system lymphomas: Pattern and prognostic impact: J Neurol, 2018; 265(3); 647-58
10.. Wu YW, Zheng J, Liu LL, Imaging of hemorrhagic primary central nervous system lymphoma: A case report: World J Clin Cases, 2020; 8(15); 3329-33
11.. Arita K, Kurisu K, Tominaga A, Relationship between intratumoral hemorrhage and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in pituitary adenoma: Hiroshima J Med Sci, 2004; 53; 23-27
12.. Sita-Lumsden A, Harris P, Bower M, Lymphoma in the immunocompromised: Br J Hosp Med, 2010; 71(5); 264-68
Figures
In Press
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942660
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943174
19 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943136
21 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943645
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250