22 December 2021: Articles 
Successful Pregnancy and Persistent Polyclonal B Cell Lymphocytosis (PPBL): A Case Study of a Rare Co-Existence
Unknown etiology, Unusual clinical course, Rare coexistence of disease or pathology
Georgios Dryllis1ABF, Theofanis Giannikos2F, Eliana A. Konstantinou2F, Ioannis Moustakas2F, Panagiotis Christopoulos3F, Theodoros Pittaras2F, Marianna Politou2EF, Serena Valsami2ABDEFG*DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.933746
Am J Case Rep 2021; 22:e933746
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Persistent polyclonal B cell lymphocytosis (PPBL) is a benign clinical condition, which is characterized by persistent absolute polyclonal B lymphocytosis (>4.0 K/μL), with the presence of circulating binucleated lymphocytes on the peripheral blood smear and an extra 3 chromosome long arm i(3q) in most cases. Immunophenotype reveals the polyclonal population of B cell lymphocytes with expression of CD19, CD20, and CD22 antigens, and κ and λ immunoglobulin light chains. Patients are mostly asymptomatic. Although PPBL has a benign clinical course and does not affect the survival expectancy of most patients, pregnancy seems to be extremely rare in these patients, as only 1 case reported so far. Although the real role of immunologic disorders, possibly PPBL, in recurrent pregnancy losses remains unclear, the rarity of successful pregnancy in PPBL patients could be attributed to the possible association of PPBL with infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
CASE REPORT: In the present study we present the second published case of a woman with a typical PPBL and recurrent pregnancy loss with a successful pregnancy outcome. Close clinical and laboratory monitoring in combination with the administration of thromboprophylaxis and the induction of mild immunosuppression with low-dose prednisolone may have contributed to the successful outcome of the pregnancy.
CONCLUSIONS: In conclusion and taking all these findings into consideration, pregnancy in patients with PPBL seems to be extremely rare and the contribution of PPBL to the 2 previous miscarriages in our case could not be excluded.
Keywords: Abortion, Spontaneous, Lymphocytosis, Lymphoma, B-Cell, Anticoagulants, B-Lymphocytes, Female, Humans, Immunophenotyping, Pregnancy, venous thromboembolism
Background
Persistent polyclonal B cell lymphocytosis (PPBL) is a clinical entity that was originally described by Gordon et al [1] in 1982 as a syndrome. It is a benign clinical condition characterized by persistent absolute lymphocytosis (>4.0 K/μL) and a moderate increase of polyclonal IgM. The presence of circulating binucleated lymphocytes on a peripheral blood smear is the basic characteristic of this syndrome. PPBL is diagnosed almost exclusively among middle-aged women, usually heavy smokers (up to 98%). Patients are asymptomatic with no signs on clinical examination aside from mild splenomegaly in some cases [2,3].
Immunophenotype reveals the polyclonal population of B cell lymphocytes with expression of CD19, CD20, and CD22 antigens and κ and λ immunoglobulin light chains. In most cases, CD27, IgM, and IgD, antigens associated with the central memory cells are also detected on the cell surface [2].
Cytogenetic analysis reveals the presence of i3q, an extra 3 chromosome long arm i(3q), among most of the patients, which is considered a specific marker of PPBL. Additional abnormalities (ie, trisomy 3, duplications of the long arm of chromo-some 3, chromosome 3 instability, and abnormalities of other chromosomes, del(6q), +der(8) or +8, polyploid karyotype) have been also described [4–7]. BCL2/IgH rearrangements are also commonly detected. The presence of HLA-DR7 in over the two-third of patients with PPBL shows that there is a very strong possibility of this syndrome having a genetic predisposition, and binucleated lymphocytes can be found in asymptomatic family members [8,9].
However, the cause of PPBL remains unknown and an association with cigarette smoking has been suggested. It is worth mentioning that in 1 reported case, the lymphocytosis resolved after stopping smoking and returned on restarting [7,10,11].
PPBL is a disorder with unknown incidence that is probably underdiagnosed, as most patients are asymptomatic [2]. PPBL remains in most cases a benign disorder, as most patients (89%) remain free of symptoms or complications after long-term follow-up [7,8]. However, PPBL has several characteristics associated with malignant tumors, such as the occurrence of cytogenetic abnormalities and the frequently observed chromosomal instability. The occurrence of subsequent malignancies (mainly non-Hodgkin lymphomas, lung cancer, and MGUS) occurs in up to 12% of patients according to a long-term follow-up of 150 patients [7]. The role of tobacco seems to be dominant. Taking into consideration that tobacco use is a well-recognized risk factor for carcinogenesis, and that PPBL patients are mostly heavy smokers, tobacco could be a confounding factor in interpreting the real link between PPBL and subsequent malignancies [7].
It is worth noticing that aside from the fact that PPBL remains in most cases a benign disorder with indolent clinical course, pregnancy seems to be extremely rare in PPBL patients, and to the best of our knowledge, only 1 such case has been reported in the literature so far [10].
In the present study, we report the second case of a woman with typical PPBL and recurrent pregnancy loss with a successful pregnancy outcome.
Case Report
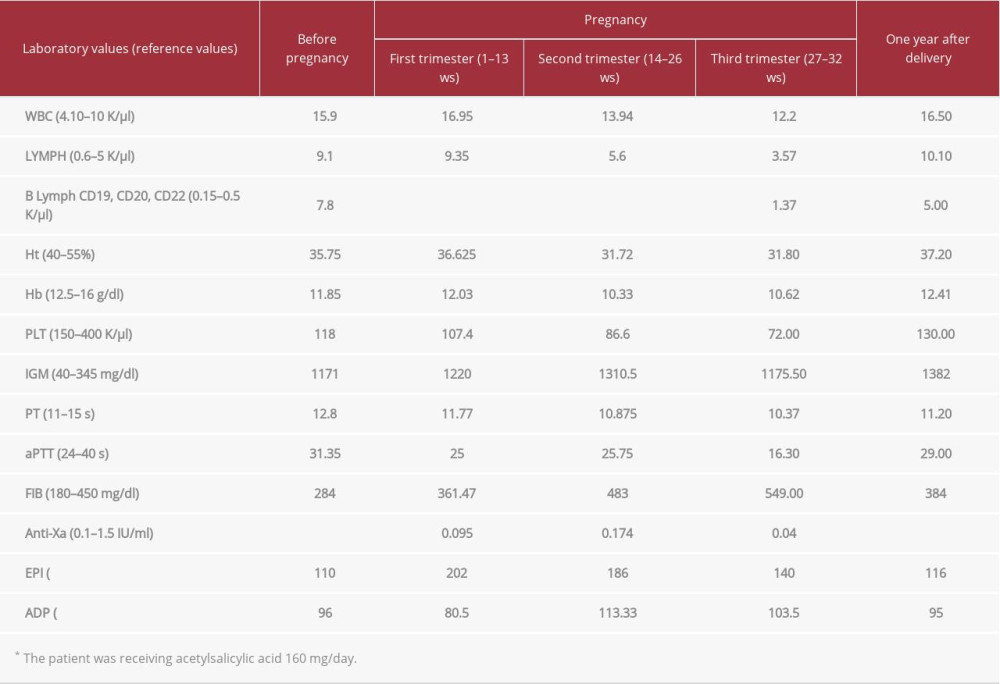
A 38-year-old woman was referred to our hospital in October 2016 after a pregnancy failure in the 8th week of gestation. She was an active smoker and her medical history included 2 episodes of pneumonia during the past year. There was no personal or family history of thrombosis. She had no symptoms and no palpable spleno-hepatomegaly or lymphadenopathy on physical examination. Full blood count at presentation revealed leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, and mild thrombocytopenia without significant anemia (WBC 17.5×109/L, Neut 4.85×109/L, lymph 8.5×109/L, Mono 3.95×109/L, Hct 36.1%, PLT 118 K/μL). Peripheral blood smear examination showed lymphocytosis with the presence of irregular lymphocytes; binucleated and bilobated cells comprising 10% of lymphocytes (Figure 1). A polyclonal increase of serum IgM (1200 mg/dl, normal range 40–300 mg/dl) was present, with normal IgG and IgA levels. Immunophenotyping demonstrated a polyclonal population of B lymphocytes (7.8 KμL) positive for IgM, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD79b, and FMC7 and negative for CD5, CD10, CD23, and CD43, with polyclonal expression of surface immunoglobulin k and l light chains (ratio: 1.5). The patient had HLA-DR 11/11. Cytogenetic and FISH analysis revealed the presence of isochromosome i(3)(q10), which characterizes PPBL. An abdominal ultrasound showed a mild hepatomegaly of 15.4 cm and a mild splenomegaly of 15.4 cm. Based on the above-mentioned findings, a diagnosis of persistent polyclonal B cell lymphocytosis (PPBL) was made.
At the same time our patient was diagnosed with in situ cervical cancer in which 3 different types of HPV were detected by RT-PCR: HPV 39, 16, and 68. She was treated with large loop excision of the transformation zone loop by electrosurgical excision procedure.
Six months later, the patient had a second miscarriage in the 8th week of gestation. She underwent a thrombophilia screening; plasma ATIII and protein C activity were normal, free protein S level was 51.2% (normal range: 55–130%) and she tested negative for factor V Leiden and factor II G20210A mutations. Homocysteine levels were within normal values. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome was excluded because anticardiolipin and antiB2 GPI antibodies, both IgG and IgM, and lupus anticoagulant were negative. Testing for viral infections (HBV, HCV, HIV1 and 2), hormone abnormalities, and connective tissue diseases was negative. All other hematological parameters remained unchanged, as depicted in Table 1. Global hemostatic assessment via thromboelastography (ROTEM) revealed a normal clotting potential (data not shown).
Six months later, the patient became pregnant for the third time. Due the past history of 2 recurrent miscarriages and taking into account her age (39 years old) and a possible mild protein S insufficiency, she was started on acetylsalicylic acid 160 mg/day, enoxaparin prophylactic dose 4.500 IU/day, prednisone10 mg/day, and progesterone 300 mg/day.
During her pregnancy the patient gave up smoking. Regarding her hematological parameters, a gradual decrease in the absolute number of lymphocytes was registered from the 12th week (Table 1). Immunophenotyping confirmed that lymphocyte reduction was due to the marked decrease (about 70%) of B lymphocytes. In the peripheral blood smear, binucleated lymphocytes were only rarely seen. The platelet count decreased to 70 K/μl, while IgM levels remained quite stable, as shown in Table 1. The spleen and liver ultrasound features remained unchanged during pregnancy.
The clotting screening with PT, aPTT, fibrinogen, ROTEM, and enoxaparin effect via anti-Xa at several time points, was normal for gestational age. Prednisolone was gradually stopped on the 18th week of gestation and on the 22nd week our patient developed a fungal skin infection that resolved with local treatment. The ultrasound examination for fetal growth on the 28th week showed possible intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR); thus, the tinzaparin dose was increased from prophylactic to intermediate. In the 32th week of gestation, she developed symptoms of premature labor and an elective Cesarean section was performed. A preterm male neonate with birth weight of 1720 g was born. The newborn was transferred to the Intensive Care Unit because of prematurity. The woman was discharged 5 days later, while the baby was discharged 4 weeks later; both being in absolute health.
One year after delivery, our patient’s blood examination showed that the lymphocytosis had relapsed and B lymphocyte numbers returned to that of the pre-gestational period.
Discussion
The case presented is the second case of a patient with PPBL with a successful pregnancy. Even though PPBL is a mild asymptomatic clinical condition with long life expectancy, only 1 case of PPBL with pregnancy has been presented so far [10].
Our patient had also in situ cervical cancer, in which 3 types of HPV were detected. Taking into consideration that the HPV genome has been detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, we looked for it in pathological lymphocytes, but unsuccessfully. Supernumerary isochromosome 3q, which plays a key role in the physiopathology and evolution of PPBL, could explain the binucleated lymphocytes and chromosomal instability. In addition, according to previous studies, isochromosome 3q is also involved in the progression of cervical carcinomas; especially when cells exhibit either tetrasomy or aneusomy for chromosomes 3 and 17, in which there is a significant increase in disease progression [11–13]. The contribution of isochromosome 3 in cervical cancer development in our patient, albeit the presence of HPV genome, could not be excluded.
Due to 2 consecutive pregnancies losses, our patient underwent a diagnostic work-up that excluded possible known causes of gestation failures at the first trimester such as antiphospholipid syndrome, hereditary thrombophilia, uterus abnormalities, thyroid dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, and chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus [14–16]. Although antiphospholipid antibodies of immunoglobulin (IgM) isotype or lupus anticoagulant were also reported in a few PPBL cases, our patient tested negative twice [8]. The fact that no other clinical etiology for the miscarriage was found was not surprising, as the almost 50% of recurrent pregnancy losses exhibit normal laboratory values and the cause remains elusive [16].
Considering the rarity of reported pregnancies in PPBL (only 1 case so far) [7], there may have been a negative contribution of the disease to a successful pregnancy. B cell compartment and its functions are suppressed during pregnancy, and they lose their responsiveness to mitogens, leading to a significant interference in normal pregnancy with B lymphocyte kinetics and functions [10]. Several studies have shown that alteration in immune cells or autoantibodies lead to higher risk of recurrent pregnancy loss and that several immunological factors affect embryo implantation. However, except for antiphospholipid syndrome, the real role of immunologic disorders, possibly PPBL, in recurrent pregnancy losses remains unclear [16]. Additionally, it is worth mentioning that since PPBL affects mainly female adults with a median age at diagnosis of 40–50 years [4], it appears that age could also be a factor contributing to the rarity of reported pregnancy in this population.
Infertility and pregnancy loss is a well-recognized phenomenon in other blood disorders affecting B lymphocytes, such as lymphoproliferative diseases (ie, Hodgkin lymphoma and B NHLs). Infertility in these cases, which is due to both the disease (ie, azoospermia in males, reduced ovarian reserve, premature menopause in females) and the anticancer treatment, is reversible in most cases [17].
Based on the 2 previous consecutive pregnancy losses, our patient received a prophylactic dose of low-molecular-weight heparin and aspirin after her positive pregnancy test. Although in some studies the daily administration of low-molecular-weight heparin and low-dose aspirin during pregnancy has shown no difference in pregnancy complications, neonatal outcome, or adverse effects, the combination has been proven effective in some women with recurrent miscarriages and acquired or inherited thrombophilia [18,19]. In addition, heparin in combination with aspirin may increase the live birth rate in women with recurrent pregnancy loss and a non-criteria obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome, but further research is needed [16].
Our patient also received prednisolone. The proposed favorable role of corticosteroids in pregnancy regards the establishment of early pregnancy by suppressing uterine natural killer (uNK) cells and thus improving trophoblast invasion and proliferation. Increased NK cells are found in peripheral blood and locally in the endometrium (uNK) of women with recurrent miscarriages, compromising the trophoblast invasion; NKs express glucocorticoid receptors and thus prednisolone has been used as a therapeutic agent as it does not affect the fetus by not passing through the placenta [20,21]. Adverse effects of prednisolone treatment during pregnancy include a higher risk of diabetes and hyper-tension and a higher risk of preterm birth. In our case, at 28 weeks of gestation, the fetus developed signs of IUGR and the woman had a preterm birth at 32 weeks. However, since prednisolone adverse reactions are dose-dependent and that low doses (<10 mg/kg daily) have not been associated with premature birth, the contribution of low-dose prednisolone treatment to premature birth in our case is rather unlikely [22,23]. On the contrary, the beneficial effect of prednisolone administration through mild immunosuppression in the early stages of pregnancy in our case seems to be more likely.
It is worth mentioning that during the course of the pregnancy in our case, a significant decrease of absolute number of lymphocytes, in particular B lymphocytes, was noted; B cells at diagnosis: 7.8 Kμl and at labor: 1.376 K/μl: an 83% decrease, while 1 year after delivery, B cell absolute number raised to 5.0 K/μl. Although the additional putative effect of corticosteroids on the reduction of lymphocytes cannot either be excluded, this phenomenon is part of the tolerant–anti-inflammatory immune response in normal pregnancies, as previously described [10]. It has been shown that the number of peripheral lymphocytes decreases gradually during pregnancy, with lowest values at about the 7th month of pregnancy. In particular, B lymphocytes are suppressed during pregnancy at the early stage of B lymphopoiesis due to the actions of estrogens [24,25]. Such a pattern has also been observed in a previous case of pregnancy in PPBL, leading to a clear reduction in the absolute number of B cells and to reversal of central memory B cell expansion, which is the main characteristic of the polyclonal B cell population in PPBL [10].
Conclusions
In conclusion, and taking all these findings into consideration, we pregnancy in patients with PPBL seems to be extremely rare, and the contribution of PPBL to the 2 past miscarriages of our pregnant could not be excluded. The fact that only 2 cases of successful pregnancy in patients with persistent polyclonal B lymphocytosis have been reported to date could be attributed to the possible association of the disease with infertility and/or the occurrence of miscarriages, as in our case. The rarity of PPBL diagnosis makes it difficult to prove such an association, while the age at diagnosis of patients with PPBL is a factor that cannot be overlooked. Close clinical and laboratory monitoring of our patient in combination with the administration of thromboprophylaxis and the induction of mild immunosuppression with low-dose prednisolone may have contributed to the successful outcome of the pregnancy.
References:
1.. Gordon DS, Jones BM, Browning SW, Persistent polyclonal lymphocytosis of B lymphocytes: N Engl J Med, 1982; 307(4); 232-36
2.. Troussard X, Flandrin G, Chronic B-cell lymphocytosis with binucleated lymphocytes (LWBL): A review of 38 cases: Leuk Lymphoma, 1996; 20(3–4); 275-79
3.. Troussard X, Valensi F, Debert C, Persistent polyclonal lymphocytosis with binucleated B lymphocytes: A genetic predisposition: Br J Haematol, 1994; 88(2); 275-80
4.. Callet-Bauchu E, Gazzo S, Poncet C, Distinct chromosome 3 abnormalities in persistent polyclonal B-cell lymphocytosis: Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 1999; 26(3); 221-28
5.. Mossafa H, Malaure H, Mayandie M, Persistent polyclonal B lymphocytosis with binucleated lymphocytes: A study of 25 cases. Groupe Français d’Hématologie Cellulaire: Br J Haematol, 1999; 104(3); 486-93
6.. Mossafa H, Tapia S, Flandrin G, Chromosomal instability and ATR amplification gene in patients with persistent and polyclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (PPBL): Leuk Lymphoma, 2004; 45(7); 1401-6
7.. Cornet E, Mossafa H, Courel K, Persistent polyclonal binucleated B-cell lymphocytosis and MECOM gene amplification: BMC Res Notes, 2016; 9; 138
8.. Troussard X, Cornet E, Lesesve JF, Polyclonal B-cell lymphocytosis with binucleated lymphocytes (PPBL): Onco Targets Ther, 2008; 1; 59-66
9.. Cornet E, Lesesve JF, Mossafa H, Long-term follow-up of 111 patients with persistent polyclonal Bcell lymphocytosis with binucleated lymphocytes: Leukemia, 2009; 23; 419-22
10.. Carulli G, Ciancia EM, Sammuri P, Modifications in B-lymphocyte number and phenotype in the course of pregnancy in a woman with persistent polyclonal B-cell lymphocytosis: A flow cytometric study: J Clin Exp Hematop, 2015; 55(2); 77-82
11.. Heselmeyer K, Macville M, Schröck E, Advanced-stage cervical carcinomas are defined by a recurrent pattern of chromosomal aberrations revealing high genetic instability and a consistent gain of chromosome arm 3q: Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 1997; 19(4); 233-40
12.. Heselmeyer K, Schröck E, du Manoir S, Gain of chromosome 3q defines the transition from severe dysplasia to invasive carcinoma of the uterine cervix: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996; 93(1); 479-84
13.. Olaharski AJ, Sotelo R, Solorza-Luna G, Tetraploidy and chromosomal instability are early events during cervical carcinogenesis: Carcinogenesis, 2006; 27(2); 337-43
14.. Oliver A, Overton C, Diagnosis and management of miscarriage: Practitioner, 2014; 258(1771); 25-28 , 23
15.. Robinson GE, Pregnancy loss: Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2014; 28(1); 169-78
16.. Vomstein K, Feil K, Strobel L, Immunological risk factors in recurrent pregnancy loss: guidelines versus current state of the art: J Clin Med, 2021; 10(4); 869
17.. Viviani S, Caccavari V, Gerardi C, Male and female fertility: Prevention and monitoring Hodgkin’ lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma adult survivors. A systematic review by the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi: Cancers, 2021; 13; 2881
18.. McNamee K, Dawood F, Farquharson RG, Thrombophilia and early pregnancy loss: Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2012; 26(1); 91-102
19.. Visser J, Ulander VM, Helmerhorst FM, Thromboprophylaxis for recurrent miscarriage in women with or without thrombophilia. HABENOX: A randomised multicentre trial: Thromb Haemost, 2011; 105(2); 295-301
20.. Michael AE, Papageorghiou AT, Potential significance of physiological and pharmacological glucocorticoids in early pregnancy: Hum Reprod Update, 2008; 14(5); 497-517
21.. Tang AW, Alfirevic Z, Turner MA, Prednisolone trial: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial of prednisolone for women with idiopathic recurrent miscarriage and raised levels of uterine natural killer (uNK) cells in the endometrium: Trials, 2009; 10; 102
22.. Bramham K, Thomas M, Nelson-Piercy C, First-trimester low-dose prednisolone in refractory antiphospholipid antibody-related pregnancy loss: Blood, 2011; 117(25); 6948-51
23.. Palmsten K, Rolland M, Hebert MF, Patterns of prednisone use during pregnancy in women with rheumatoid arthritis: Daily and cumulative dose: Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf, 2018; 27(4); 430-38
24.. Nguyen TG, Ward CM, Morris JM, To B or not to B cells-mediate a healthy start to life: Clin Exp Immunol, 2013; 171(2); 124-34
25.. Valdimarsson H, Mulholland C, Fridriksdottir V, Coleman DV, A longitudinal study of leucocyte blood counts and lymphocyte responses in pregnancy: A marked early increase of monocyte-lymphocyte ratio: Clin Exp Immunol, 1983; 53(2); 437-43
In Press
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942770
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943214
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943010
16 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943687
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250