30 January 2023: Articles 
Methanol Intoxication-Associated Brain Hemorrhages: Can Early Detection Be Life-Saving? A Case Report
Challenging differential diagnosis, Unusual or unexpected effect of treatment, Rare disease, Educational Purpose (only if useful for a systematic review or synthesis), Rare coexistence of disease or pathology
Megan E. Decker1EF, Nicholas D. Briski2EF, Amira Salem3E, Emad Noor2FG, Abdallah Khashan3EF*DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.938749
Am J Case Rep 2023; 24:e938749
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Methanol can cause many acute complications when ingested, either intentionally or accidentally. One rare complication is cerebral hemorrhage, which can present with focal neurologic deficits, decreased consciousness, and fixed, dilated pupils. With vigilant monitoring of patients in the acute period of toxicity, rapid identification, and initiation of treatment, outcomes can potentially be improved in these patients.
CASE REPORT: We present a case of a 42-year-old man who presented after ingestion of windshield wiper fluid. Initial symptoms started with fatigue and altered mental status, but he quickly developed abdominal pain and became obtunded. CT initially showed no acute hemorrhage or other pathology, but on day 2, despite receiving fomepizole, bicarbonate, and dialysis, the patient became hypotensive and showed loss of cranial nerve reflexes, and repeated CT head scans showed acute intracranial hemorrhage with mass effect.
CONCLUSIONS: Although the exact mechanism of intracranial hemorrhage and necrosis following methanol intoxication remains uncertain, we know beyond doubt that it can progress rapidly and lead to severe and irreversible complications, so identifying and treating it immediately is essential. In this case, methanol ingestion was known on presentation, antidote and renal replacement therapy were initiated within hours of ingestion, yet our patient still suffered fatal brain hemorrhage. Important warning signs of acute hemorrhage include loss of cranial nerve reflexes and decrease in consciousness, so these findings warrant further evaluation and prompt neuroimaging, especially in high-risk patients like the one in this report.
Keywords: Intracranial Hemorrhages, Poisoning, Male, Humans, Adult, Methanol, Renal Dialysis, Cerebral Hemorrhage
Background
Methanol is an alcohol found in commercial paint thinners, organic fluids, and windshield-cleaner products. It is similar to ethanol in smell and taste, making methanol-containing fluids a simple alcohol alternative, except that it is highly toxic and even lethal. During the year 2016 there were an estimated 106 683 deaths from unintentional methanol toxicity, and without adequate treatment its mortality has been estimated at 40% [1]. Cerebral hemorrhage is a relatively rare complication of this ingestion, occurring in the acute setting in about 13.5% of cases, though a publication based on data from the Czech Republic suggests that hemorrhagic lesions also occurred in the chronic setting months after the initial ingestion in as many as 33% of patients who survived the initial hospitalization [2]. Further, those with evidence of hemorrhage were associated with more severe clinical course as indicated by higher acidemia and lactic acidosis. Methanol poisoning more commonly causes visual disturbances and severe metabolic acidosis and, in unfortunate instances, causes intracranial hemorrhage and death. Formic acid, which is methanol’s most offensive metabolite, causes irreversible neurological damage. We report a case of methanol-induced intracranial hemorrhage.
Case Report
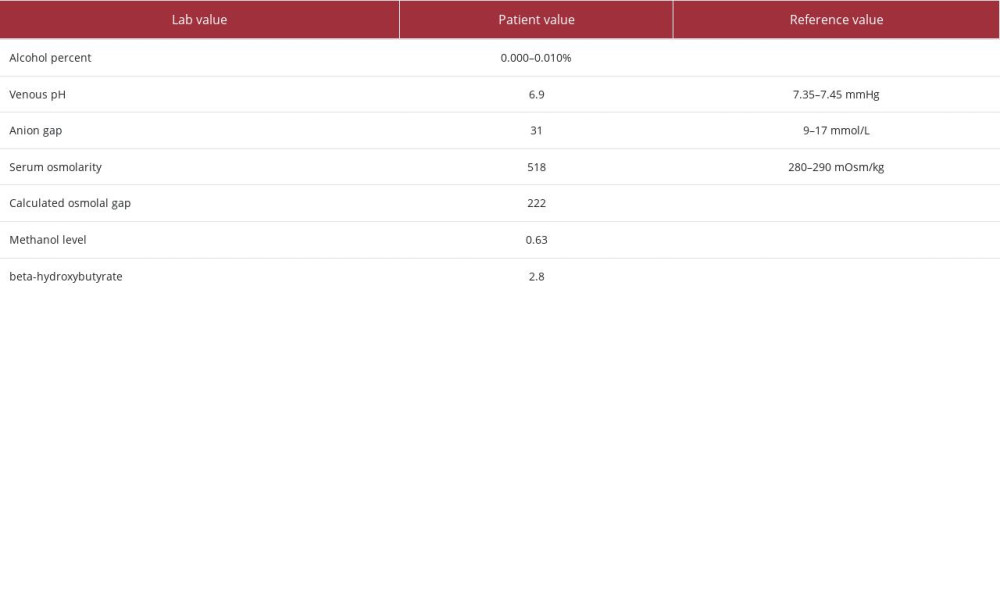
A 42-year-old man with past medical history of hypertension, depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety, presented to the Emergency Department with altered mental status due to intentional ingestion of windshield wiper fluid. He was restless and according to emergency medical services, he was having of generalized abdominal pain and denied suicidal ideation. Initial vital signs documented on arrival to the Emergency Department were blood pressure 134/81 mmHg, heart rate 98 beat per minute, temperature 36.4°C, and oxygen saturating 100% on room air, in no respiratory distress. On arrival to the Emergency Department, he said he felt tired. The physical examination was unremarkable. He later developed severe generalized abdominal pain and proceeded to become obtunded, with a Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) of 3, for which he was intubated. Significant laboratory test results upon admission (hospital day 0) are shown Table 1.
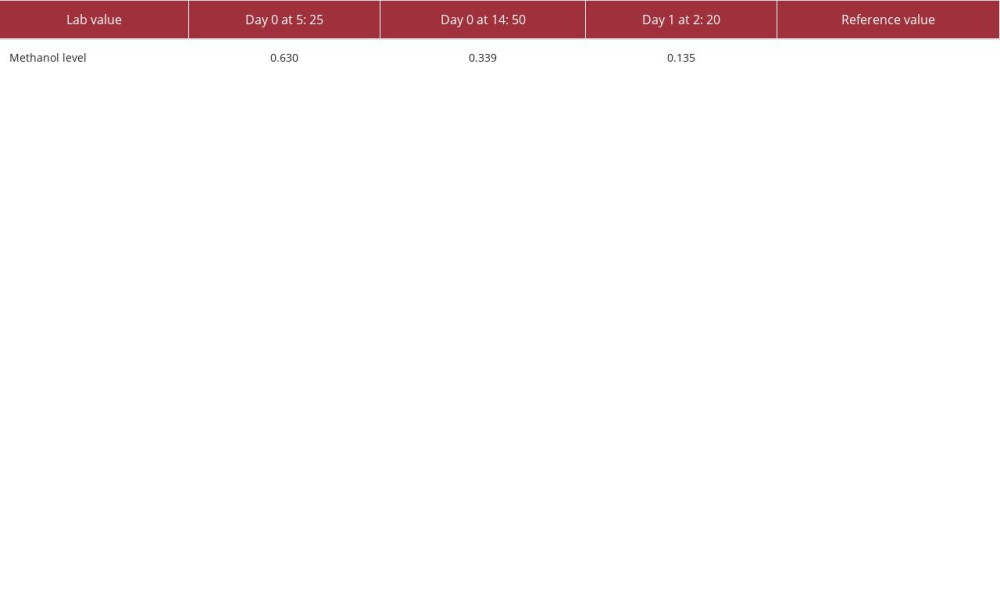
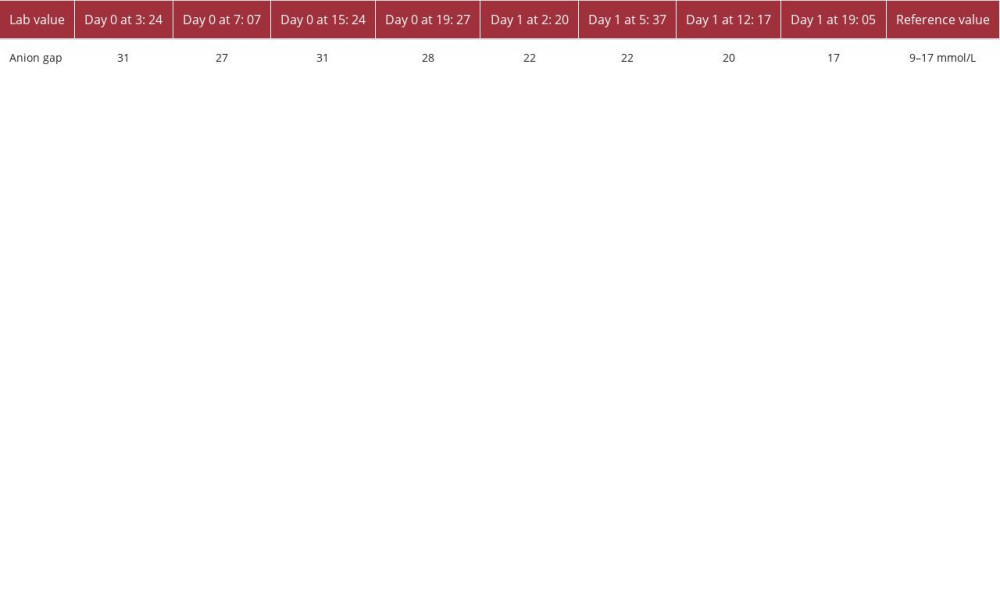
The Poison Control Center was contacted and suggested starting fomepizole and bicarbonate drip. A computed tomography (CT) scan on admission was ordered for altered mental status, showing no acute intracranial hemorrhage, significant mass effect, or acute evolving large-vessel territory infarct. Eight hours of ultrafiltration hemodialysis was performed on day one. Based on the drop in the methanol level (Tables 2, 3),
Poison Control suggested another session of hemodialysis for 4 more hours, to continue fomepizole every 12 hours, and to stop bicarbonate drip.
The patient’s blood pressure dropped to 75/35 mmHg during dialysis, so hemodialysis was discontinued after 3.5 hours, and 1 liter of normal saline bolus was ordered and administered. Upon re-assessment about 15 minutes later, his pupils were fixed and dilated and he did not have cough or gag reflexes, with a GCS of 3. A CT scan of the head (Figure 1) was ordered immediately for acute deterioration, which showed large right basal ganglia intra-parenchymal hemorrhage with intra-ventricular extension associated with right to left mid-line shift. Brain death was suspected. The patient did not exhibit any brain stem reflexes, and nuclear brain blood flow did not visualize brain uptake, which ultimately confirmed brain death. The patient was declared brain dead about 46 hours after presenting at the Emergency Department.
Discussion
Methanol is a toxic alcohol often involved in both accidental and intentional ingestions. It can be found in homemade liquor, industrial solvents, antifreeze, and windshield wiper fluid [3]. Methanol can also be found as a contaminate in products like hand sanitizers. Standard windshield wiper fluid contains 30–50% methanol, making methanol the most likely cause for toxicity in our patient [4]. Other toxic substances like ethylene glycol may be present in smaller amounts in windshield wiper fluid. Cases of methanol ingestion can be either accidental or intentional, such as in suicide attempts. Additionally, because it causes similar euphoric and intoxicating effects as ethanol, it is sometimes also consumed recreationally as a substitute for ethanol due to its low cost and easy accessibility. According to the annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers, in the United States in 2020, there were over 700 reported cases of methanol poisoning, resulting in at least 11 deaths [5].
Methanol is structurally similar to and produces similar effects to ethanol, but it is processed differently in the body. As methanol is metabolized and converted to formic acid 12–15 hours after initial ingestion, its toxic effects begin. Common signs and symptoms of methanol intoxication include blurry vision, partial or “snow” blindness, hypotension, dizziness, confusion, agitation, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, seizures, and coma [3]. Significant toxicity results in high anion gap metabolic acidosis, elevated osmolar gap, and end-organ damage [3]. Without appropriate treatment, a dose of 1 g/kg of methanol or ethylene glycol can be fatal, although serious complications can be seen with much smaller quantities [6].
One of the rare potential adverse effects of methanol intoxication is cerebral hemorrhage. Reports of the incidence of methanol intoxication-induced brain hemorrhage vary but range from 13.5% [7] to 33% [2] of patients hospitalized for methanol poisoning. The mechanism of methanol-induced brain hemorrhage is not fully understood, but one hypothesis is that formic-acid-induced inhibition of cytochrome oxidase in cell mitochondria leads to necrosis, particularly in areas of the brain like the putamen with high metabolic demands [3]. These areas of necrosis may then be more vulnerable to hemorrhage. Patients with brain hemorrhage typically present acutely with decreased consciousness, unresponsiveness, and fixed, dilated pupils. The diagnosis is confirmed with a non-contrast CT of the head, where evidence of brain necrosis and hemorrhage indicates a particularly poor prognosis.
Methanol’s toxic effects are a result of formic acid production when methanol is metabolized. Therefore, one approach for mitigating the damage involves limiting its metabolism by inhibiting an enzyme upstream of its production by using fomepizole, an inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase. Hemodialysis is also often indicated in cases of methanol poisoning with severe metabolic acidosis or evidence of organ damage, such as cerebral infarction or hemorrhage. Cerebral hemorrhage is typically treated in the intensive care unit with reversing anticoagulation, close monitoring and management of blood pressure, and measures to decrease intracerebral pressure such as elevating the head of the bed, sedation, and antipyretics.
Here, we report a rare case of cerebral hemorrhage induced by methanol intoxication. By reporting this case, more awareness can be spread about this complication of methanol ingestion, allowing for potentially faster identification of this complication, quicker treatment, and the ability to compare outcomes with the potential to improve outcomes for future patients. Studies have suggested the potential need to minimize or avoid heparin administration during hemodialysis, to decrease the risk of hemorrhage associated with methanol poisoning [7]. However, this hypothesis is under debate. A 2016 study specifically looking at this issue found no association between brain hemorrhages and systemic anticoagulation during dialysis [2].
Patients and their physicians would benefit from the results of further investigation into the best ways to prevent and treat methanol-induced cerebral hemorrhage and increased awareness of hemorrhage as a complication of methanol ingestion. Additionally, knowledge of early, subtle signs and symptoms can significantly reduce morbidity and mortality. When providers encounter patients with decreased consciousness, especially with metabolic acidosis and increased anion gap, toxic methanol ingestion should be considered. Patients with probable or confirmed methanol intoxication should be admitted to the intensive care unit for close monitoring and early intervention if they show signs of decompensation, particularly decreased consciousness, unresponsiveness, or fixed, dilated pupils suggestive of an intracranial bleed. Treatment with hemodialysis and fomepizole have been shown to help improve patient outcomes and should be considered by providers who encounter these patients.
Conclusions
Although the exact mechanism of intracranial hemorrhage and necrosis following methanol intoxication remains uncertain, we know beyond doubt that it can progress rapidly and lead to severe and irreversible complications, so identifying and treating it immediately is essential. In this case, methanol ingestion was known on presentation, and antidote and renal replacement therapy were initiated within hours of ingestion, yet our patient still suffered fatal brain hemorrhage. Important warning signs of acute hemorrhage include loss of cranial nerve reflexes and decrease in consciousness, so these findings warrant further evaluation and prompt neuroimaging, especially in high-risk patients like the one in this report.
References:
1.. Singh A, Samson R, Girdhar A, Portrait of a methanol-intoxicated brain: Am J Med, 2011; 124(2); 125-27
2.. Zakharov S, Kotikova K, Vaneckova M, Acute methanol poisoning: Prevalence and predisposing factors of haemorrhagic and non-haemorrhagic brain lesions: Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2016; 119(2); 228-38
3.. Gallagher N, Edwards FJ, The diagnosis and management of toxic alcohol poisoning in the Emergency Department: A review article: Adv J Emerg Med, 2019; 3(3); e28
4.. Weiner S, Toxic alcohols: Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 2011; 1400-10, New York, McGraw Hill
5.. Gummin DD, Mowry JB, Beuhler MC, 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report: Clin Toxicol (Phila), 2021; 59(12); 1282-501
6.. Aisa TM, Ballut OM, Methanol intoxication with cerebral hemorrhage: Neurosciences (Riyadh), 2016; 21(3); 275-77
7.. Phang PT, Passerini L, Mielke B, Brain hemorrhage associated with methanol poisoning: Crit Care Med, 1988; 16(2); 137-40
In Press
12 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943244
13 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943275
13 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943411
13 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942864
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250