21 January 2021: Articles 
A 61-Year-Old Woman with Chronic Iron-Deficiency Anemia Due to a Cameron Lesion and a Response to Oral Application of Combined Poloxamer 407 with Hyaluronic Acid and Chondroitin Sulfate Following Single Treatment with Pantoprazole: A Case Report
Challenging differential diagnosis, Unusual setting of medical care, Rare disease
Iliyan Emilov Iliev1D*, Almute Loidl2BDOI: 10.12659/AJCR.928021
Am J Case Rep 2021; 22:e928021
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Cameron lesions are linear erosions and ulcers on the crests of gastric mucosal folds in the neck of a hiatal hernia and can be difficult to diagnose and treat. This report is of a case of chronic iron deficiency in a 61-year-old woman with a late diagnosis of a Cameron lesion, who did not respond to a single treatment with the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) pantoprazole, but was then treated with oral poloxamer 407 with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in addition to PPI.
CASE REPORT: We report the case of a 61-year-old women with recurrent iron-deficiency anemia, first diagnosed 40 years prior to her presentation at our Endoscopy Unit, and an ongoing melena. We discovered an intrahiatal gastric mucosal defect, which we at first treated with proton pump inhibitors and sucralfate. After a follow-up gastroscopy revealed the persistence of the lesion, we decided to incorporate into the treatment a gel-like substance containing, among others, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate, and observed that the lesion resolved completely.
CONCLUSIONS: This report highlights that Cameron lesions should be considered in patients with hiatal hernia who have iron-deficiency anemia and can be diagnosed on upper endoscopy. Further clinical studies are required to determine the role of combined poloxamer 407 with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in the management of Cameron lesions.
Keywords: Chondroitin Sulfates, Esophageal Diseases, Hyaluronic Acid, Adjuvants, Immunologic, Anemia, Iron-Deficiency, Chronic Disease, Drug Carriers, Gastroscopy, Hernia, Hiatal, pantoprazole, Poloxamer, proton pump inhibitors, stomach ulcer
Background
In 1986, Cameron and Higgins described linear erosions and ulcers on the crests of gastric mucosal folds in the neck of a hiatal hernia, resulting in gastrointestinal hemorrhage [1]. There is insufficient information on Cameron lesions in the published literature. The scarce data available are from single case reports or case series. Unfortunately, there are no randomized controlled studies on this topic. It is no exaggeration to mention that most textbooks in the field of internal medicine and surgery pay no attention to Cameron lesions, which is a fact that we will probably have to change soon. On the one hand, this is due to the small number of ‘Cameron’ patients worldwide and on the other hand because health care specialists do not recognize them. Even if recognized, a tissue sample from Cameron erosions or ulcers is rarely obtained, which explains the insufficient information about their histopathologic characteristics.
We report the case of a 61-year-old woman with chronic iron-deficiency with a late diagnosis of a Cameron lesion, who did not respond to a single treatment with the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) pantoprazole, but was then treated orally with combined poloxamer 407 with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in addition to PPI.
Case Report
A 61-year-old woman presented for an outpatient gastroscopy due to ongoing melena. She took no iron supplementation or drugs that could have changed the stool color. The patient reported no abdominal or defecation problems. Previous surgeries included open appendectomy. The patient had psoriasis vulgaris as a single comorbidity and was a non-smoker. A prophylactic treatment with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) was applied until 2009 because she had a stroke approximately 2 decades ago (the patient provided no medical records verifying this diagnosis).
Two previous gastroscopies (the first at age 21 years and the second approximately 15 years ago) had already been performed because of a chronic ‘intermittent’ iron-deficiency anemia which was first diagnosed about 40 years ago. Both revealed no pathologies. A colonoscopy had also already been performed, with no detectable bleeding sources. After the above-mentioned uneventful endoscopic examinations, the treating physicians attributed the iron deficiency to the excessive menstrual bleeding our patient used to have and prescribed her iron supplementation. Unfortunately, the anemia persisted after menopause. The patient had not taken any iron supplements for 5 years prior to our gastroscopy. Having in mind this medical history, we ordered blood tests. The results are shown in Table 1.
During our first gastroscopy, after an unproblematic esophageal intubation, we detected an axial hiatal hernia spreading approximately from 37 to 38 cm from the incisors, with a diameter of 2.2 cm. Advancing aborally, we saw multiple small, flat hematin spots which covered the gastric fundus and corpus, and were not present in the antral area. The duodenum was macroscopically intact.
The decisive diagnostic factor proved to be the inversion of the fibroelastic gastroscope, as a small macroscopically visible, not bleeding linear erosion within the hiatal hernia (Figure 1A) was detected. Tissue samples were collected, which revealed only signs of carditis.
A therapy with the proton pump inhibitors (PPI) pantoprazole and sucralfate was initiated for 6 weeks (pantoprazole 40 mg b.i.d. for 2 weeks, and afterwards once daily; sucral-fate 4 times daily) and an appointment for a follow-up gastroscopy was made.
At the time of the follow-up gastroscopy (6 weeks later), the patient had no complaints and no melena, and all laboratory values were within reference ranges (Table 1). During the endoscopic examination we observed, once more, multiple flat hematin spots in the proximal two-thirds of the stomach. The erosion was still visible, although half of it was covered by fibrin (Figure 1B). We obtained tissue samples from the erosion. We changed the treatment to PPI (pantoprazole 40 mg once daily) and a gel containing, among others, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and poloxamer 407 (4 times daily, 30 min postprandially, and at bedtime) for 3 months.
After the second gastroscopy, a new follow-up endoscopic appointment was made, which could not be kept due to the coronavirus crisis. We contacted the patient on the phone. She had no complaints and no melena, and after the above-mentioned 3-month period took only pantoprazole 40 mg once daily.
Eventually, a second follow-up gastroscopy was performed 7 months after the initial one. It revealed no erosion, with an intact cardiac mucosa (Figure 1C, 1D).
Discussion
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Cameron lesions are a complex phenomenon with an unclear pathogenesis. It is believed that they occur because of the combined effects of extra- and intraluminal mechanical and chemical factors. Pathogenetic factors are briefly presented in Table 2.
MORPHOLOGY:
Cameron lesions are non-peptic non-GERD-associated mucosal defects occurring on the top of gastric folds over the distal ring of a hiatal hernia (rarely proximally), most often along the lesser gastric curvature. They can be superficial (erosions) or deep (‘riding’ ulcers). Cameron lesions are typically longitudinal, but can also be oblong or ellipsoid, and never comprise the whole circumference of the hiatal hernia [14,15].
SYMPTOMS:
Most patients with Cameron lesions are older women with chronic anemia and large hiatal hernias. Since hiatal hernias are predominantly asymptomatic, they present with signs of overt (melena, hematochezia, hematemesis) or occult (iron-deficiency anemia, positive fecal occult blood test) gastrointestinal bleeding. Some patients have a medical history of recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding, with or without blood transfusions, oral intake of NSAID, or iron supplements. Rarely, they also have a peptic ulcer or esophagitis [4].
DIAGNOSTICS:
The criterion standard for the diagnosis of Cameron lesions is gastroscopy. Very often, they remain uncovered within an index gastroscopy and are detected during a second-look or repeated gastroscopy (“One only sees what one looks for. One only looks for what one knows.” Goethe). That is why each hiatal hernia should be inspected ante- and retrograde with an additional perpendicular presentation of the hernial opening where the diaphragmatic hiatus exerts the highest pressure on the gastric wall (the predominant localization of Cameron ulcers). The gastroscopist should examine the mucosa above and beneath the
There are no specific laboratory tests or imaging modalities for detecting the presence of a Cameron lesion. Blood tests could be normal or demonstrate an iron-deficiency anemia. X-ray or computed tomography may be helpful for the diagnostics of complications (e.g., perforation, volvulus, blood clots in the stomach). Under certain conditions, computed tomography angiogram or Tc-99m-labeled red blood cells scintigraphy can detect an active bleeding source (bleeding speed at least 0.5 ml/min and 0.04 ml/min, respectively). The role of capsule endoscopy remains unclear [12,14].
HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS:
To the best of our knowledge, there is only 1 published article containing a description of histopathologic changes in Cameron lesions. Katz et al. describe mucosal alterations due to mucosal vascular obstruction consistent with ischemic gastropathy, such as hemorrhagic infiltrates, fibrin thrombi, inflammatory response, sanguine micro-suffusions, sloughing of epithelial cells, atrophy of crypts, and coagulation necrosis [16].
Our first tissue sampling revealed mucosal alterations consistent with a minor chronic carditis. The results from the second sampling are shown in Figure 2.
MANAGEMENT:
The treatment of Cameron lesions (conservative or surgical) should be determined individually [3]. Because of the limited knowledge about their natural history and the small number of patients, modern medicine was unable to create strict guidelines and algorithms for their management. Literature reports range from cases of spontaneous healing to high-dose PPI treatment regimens [8].
The management of Cameron lesions depends on their clinical presentation. Currently, most authors recommend starting PPI administration as soon as the diagnosis is established. If the patient already receives PPIs once daily, their dosage/frequency of administration should be increased. If blood tests show signs of iron deficiency, iron supplementation is required. In case it has already been initiated, the iron dosage should be increased. A single iron supplementation is not sufficient [17]. By means of the above-mentioned treatment, an adequate symptom control is achieved in up to half of the patients with Cameron lesions. Of course, in case of significant bleeding and hemodynamic shock, stabilizing measures should be taken, since Cameron lesions cause life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding in up to one-third of all patients [11,18].
NSAID intake should be immediately discontinued. Some authors recommend the administration of prokinetic agents [19].
There are no strict criteria for the conversion from conservative to surgical treatment. Some specialists suggest a secondary surgical treatment in case of persistent complaints (e.g., anemia, hospitalization because of recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding or chronic blood loss) or complications (e.g., refractory bleeding, perforation, volvulus, gastric incarceration) [4]. The main goal of the surgical therapy is to eliminate the mandatory prerequisite for the occurrence of Cameron lesions – the hiatal hernia (there is no Cameron lesion without hiatal hernia.) Possible options are laparoscopic/open fundoplication±gastropexy and the recently developed single-incision transgastric underrunning (SILT) [3,9,20,21].
ENDOSCOPY:
Endoscopic hemostasis is a relevant but rarely reported non-surgical treatment option for bleeding Cameron lesions. Band ligation and clipping proved to be effective. A follow-up gastroscopy was not performed in many studies, but could be indicated when complaints persist.
OUR PATIENT:
After diagnosis establishment, we started a treatment with oral intake of PPIs (pantoprazole 40 mg b.i.d. for 2 weeks and once daily afterwards) in combination with sucralfate 4 times daily, both for 6 weeks. Since the iron panel revealed normal values, no iron supplementation was initiated. PPIs administration aims to inhibit gastric acid production; thus, its possible role in the genesis of Cameron lesions. Sucralfate is a sucrose octasulfate and aluminum hydroxide (AlOH) complex forming a viscous paste in aqueous acidic media (e.g., in the esophagus, stomach, duodenum). It adheres to defective and intact mucosa through polyvalent bridges between negatively charged sucralfate polyanions and positively charged proteins, which are present in high concentrations in mucosal lesions. It also buffers the gastric acid, inhibits the action of pepsin, and absorbs bile salts. All these properties enable sucralfate to act as an effective barrier counteracting the penetration of the above-mentioned substances. Sucralfate proved to be as effective as antacids or H2-receptor antagonists in healing peptic ulcers and in animals, but was ineffective in preventing corticosteroid-induced ulcerations. Sucralfate probably stimulates the local prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and prostacyclin (PGI2) synthesis in gastric mucosa [22,23].
Since the first follow-up gastroscopy showed no improvement, we decided to use a mixed preparation of hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and poloxamer 407. In animal models (Yorkshire pigs), this mixture exhibited positive effects on the healing process of scars left after endoscopic mucosal re-section (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and had been expected to provoke an early proliferation of collagen and elastic fibers in gastric mucosal defects, thus also contributing to ulcer healing. Furthermore, it is an acceptable low-cost alternative to the existing treatment regimens [24].
Hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are extensively used in wound treatment. Their role in the therapy of gastrointestinal lesions is a subject of continuous research. Hyaluronic acid is a non-sulfated natural glycosaminoglycan and main component of the extracellular matrix. HA is a hygroscopic macromolecule formed by the polymerization of glucuronic acid and N-acetylglucosamine disaccharide. It interacts with several cell surface receptors of malignant and non-malignant gastric mucosa. HA is involved in human innate immunity and inflammatory processes, as it takes part in leukocyte recruitment and macrophage activation. It induces dendritic cell maturation and promotes cytokine release by dendritic cells and endothelial cells. HA also possesses anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, and anti-viral properties and promotes angiogenesis. Topically applied on oral mucosa, it supports tissue hydration in inflammatory processes and mucosal response to tissue injuries that could possibly result in ulcer formation and forms a protective film over exposed mucosal nerve endings, preventing them from overstimulation. Sodium hyaluronate possesses also hemostatic properties when injected in peptic ulcers.
Chondroitin sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan consisting of repeated disaccharide units polymerized into long chains. CS is an effective inhibitor of pepsin-induced damage to stomach and duodenal mucosa and showed potent anti-inflammatory properties in animal models [25–27].
Poloxamer 407 is a water-soluble, non-ionic triblock copolymer that is liquid at room temperature and assumes a gel form at body temperature. It is often used as a drug carrier. It possesses mucoadhesive properties and does not irritate mucosal membranes. Poloxamer 407 showed no direct regenerative or antimicrobial properties but maintains a stable concentration of the substances it carries for a prolonged time [28].
Conclusions
Hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are widely used in cosmetics because of their skin regeneration properties. They also possess a proven beneficial effect on the healing of acute and chronic wounds. The role of HA and CS in the treatment of gastrointestinal mucosal pathologies has increasingly been examined over the last decade. In accordance with the published literature and the experience with our patient, we hypothesize that they could also be useful for the conservative treatment of Cameron lesions (in combination with PPI, as stated in the summary of product characteristics of the products approved for use in the gastrointestinal tract). They counteract many of the possible organic and chemical pathogenetic factors, leading to its occurrence, but, of course, cannot influence the most important mechanical factor – the hiatal hernia.
In light of the good success of HA and CS in wound healing, we hypothesize the principle that internal wounds (ulcers and mucosal lesions) could be treated like external wounds – treat ulcers like wounds (treat inside like outside). If not achieving a permanent resolution, it could at least gain us some time before surgery to stabilize the patient’s condition, which could sometimes be crucial.
This case report highlights that Cameron lesions should be considered in patients with hiatal hernia who have iron-deficiency anemia and can be diagnosed on upper endoscopy. Further clinical studies are required to determine the role of combined poloxamer 407 with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in the management of Cameron lesions.
Figures
Tables
Table 1.. Laboratory test results of our patient. The tests were performed at the time of the initial, first, and second follow-up gastroscopies.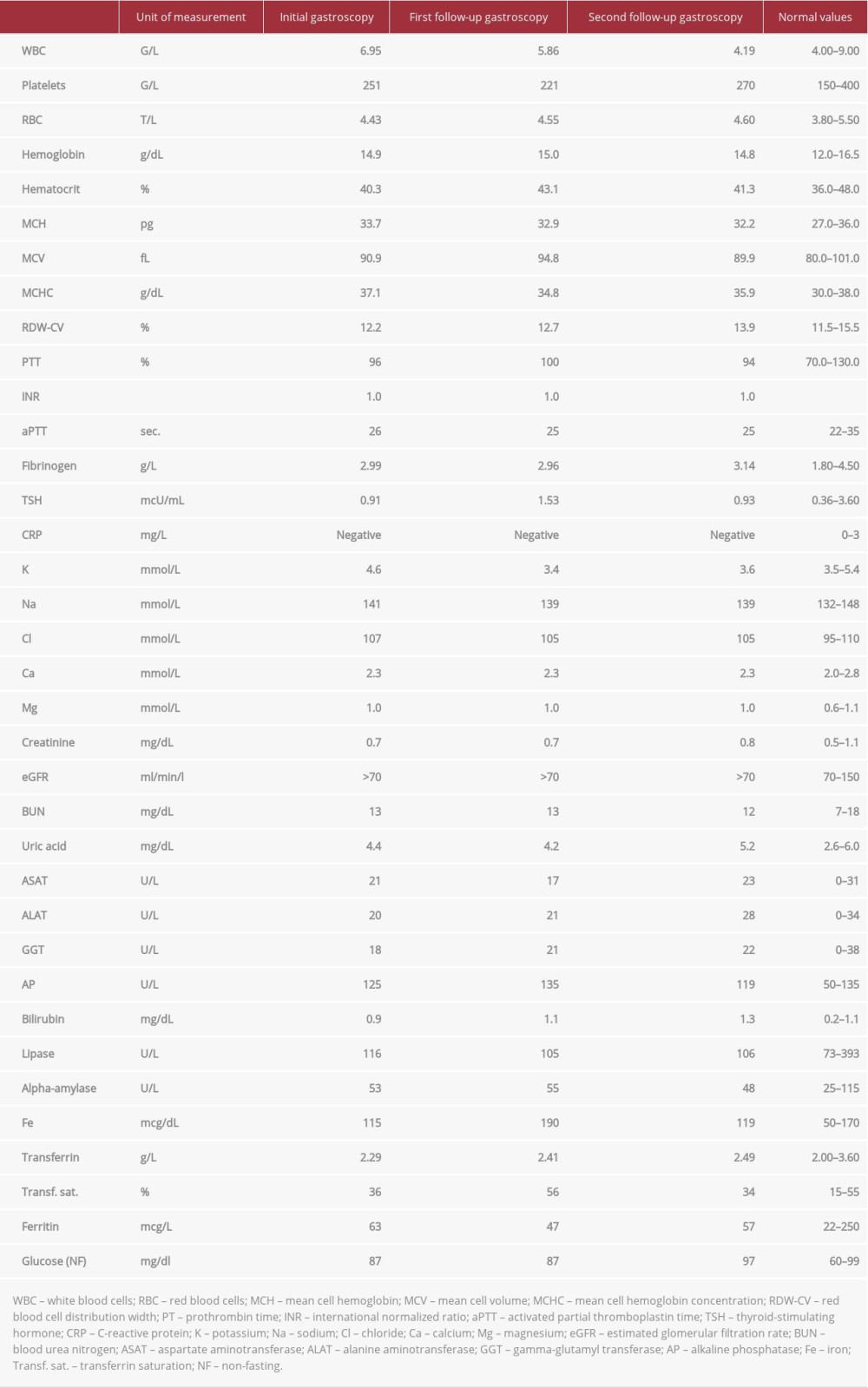 Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions.
Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions.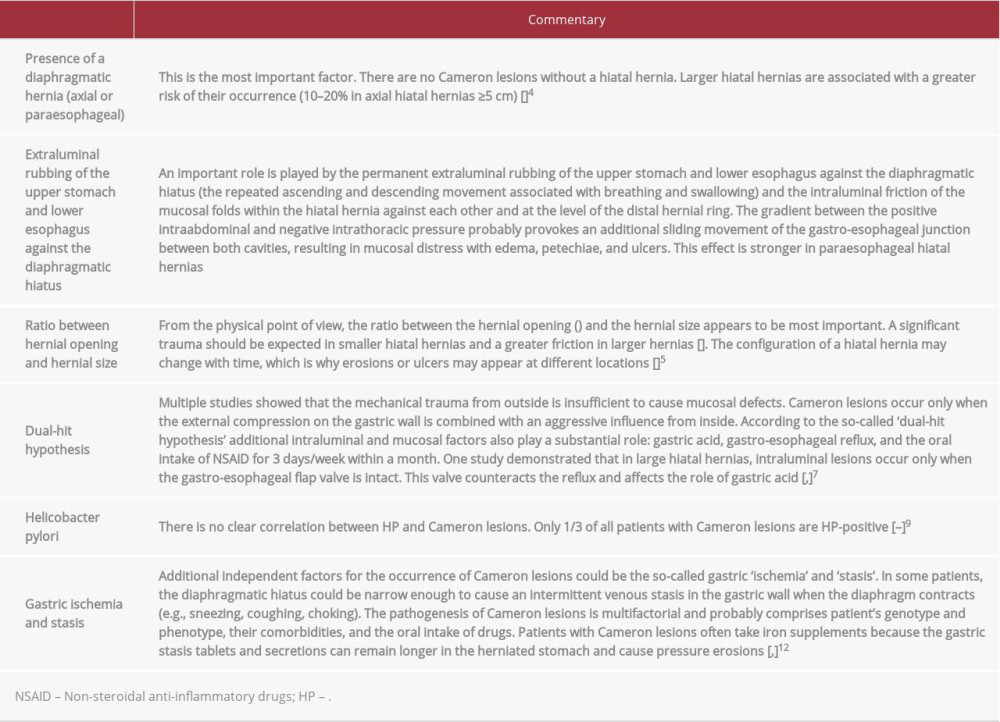
References:
1.. Cameron AJ, Higgins JA, Linear gastric erosion. A lesion associated with large diaphragmatic hernia and chronic blood loss anemia: Gastroenterology, 1986; 91; 338-42
2.. Gray DM, Kushnir V, Kalra G, Cameron lesions in patients with hiatal hernias: Prevalence, presentation, and treatment outcome: Dis Esophagus, 2015; 28(5); 448-52
3.. Kapadia S, Jagroop S, Kumar A, Cameron ulcers: An atypical source for a massive upper gastrointestinal bleed: World J Gastroenterol, 2012; 18(35); 4959-61
4.. Marine C, Dennis MJ, Gordon VO, Severe upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage from linear gastric ulcers in large hiatal hernias: a large prospective case series of Cameron ulcers: Endoscopy, 2013; 45(5); 397-400
5.. Winsor CWO, Collis JL, Anemia and hiatus hernia: Thorax, 1967; 22; 73
6.. Kimer N, Schmidt PN, Krag A, Cameron lesions: an often overlooked cause of iron deficiency anaemia in patients with large hiatal hernias: BMJ Case Rep, 2010; 2010; bcr0620103129
7.. Kaneyama H, Kaise M, Arakawa H, Gastroesophageal flap valve status distinguishes clinical phenotypes of large hiatal hernia: World J Gastroenterol, 2010; 16(47); 6010-15
8.. Zullo A, Manta R, De Francesco V, Cameron lesions: A still overlooked diagnosis. Case report and systematic review of literature: Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2018; 42; 604-9
9.. Darrell M, Gray DM, Kushnir V, Cameron lesions in patients with hiatal hernias: Prevalence, presentation, and treatment outcome: Dis Esophagus, 2015; 28(5); 448-52
10.. Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD: Sabiston textbook of surgery, 2012, Philadelphia, Elsevier Saunders
11.. Weston AP, Hiatal hernia with Cameron ulcers and erosions: Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 1996; 6(4); 671-79
12.. Morrissey JF, You see what you look for: Gastroenterology, 1986; 91(2); 481-82
13.. Winsor CWO, Collis JL, Anemia and hiatus hernia: Experience in 450 patients: Thorax, 1967; 22; 73-78
14.. Maganty K, Smith RL, Cameron lesions: Unusual cause of gastrointestinal bleeding and anemia: Digestion, 2008; 77; 214-17
15.. Gupta P, Suryadevara M, Das A, Cameron ulcer causing severe anemia in a patient with diaphragmatic hernia: Am J Case Rep, 2015; 16; 733-36
16.. Jordan K, Sonia B, Jagmohan SS, Histopathological characterization of a Cameron lesion: Int J Surg Pathol, 2012; 20(5); 528-30
17.. Weston AP, Hiatal hernia with Cameron ulcers and erosions: Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 1996; 6(4); 671-79
18.. Moskovitz M, Fadden R, Min T, Large hiatal hernias, anemia, and linear gastric erosion: Studies of etiology and medical therapy: Am J Gastroenterol, 1992; 87; 622
19.. Hernandez GH, Soto ICF, Garcia CAJ, Cameron lesions: Keep in mind in chronic anemia: J Hepatol Gastroint Dis, 2016; 2; 2
20.. Tan CHN, Kim G, So J, Single-incision laparoscopic transgastric under-running and closure of Cameron ulcers in acute gastrointestinal bleeding: J Gastrointest Surg, 2018; 22(3); 553-56
21.. Panzuto F, Di Giulio E, Capurso G, Large hiatal hernia in patients with iron deficiency anaemia: A prospective study on prevalence and treatment: Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2004; 19; 663
22.. Arronson JK: Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs The international encyclopedia of adverse drug reactions and interactions, 2016, New York, Elsevier Science
23.. Nagashima R, Mechanisms of action of sucralfate: J Clin Gastroenterol, 1981; 3(Suppl. 2); 117-27
24.. Córdova H, Cuatrecasas M, García-Rodríguez A, Successful outcomes of a new combined solution of hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate and poloxamer 407 for submucosal injection: animal survival study: Endosc Int Open, 2019; 7(4); E576-82
25.. Kappor P, Sachdeva S, Sachdeva S, Topical hyaluronic acid in the management of oral ulcers: Indian J Dermatol, 2011; 56(3); 300-2
26.. Ianniti T, Morales-Medina JS, Merighi A, A hyaluronic acid- and chondroitin sulfate-based medical device improves gastritis pain, discomfort, and endoscopic features: Drug Deliv Transl Res, 2018; 8(5); 994-99
27.. Cho YK, Kim CS, Kim SY, The hemostatic effect of endoscopic sodium hyaluronate injection in peptic ulcer bleeding: Hepatogastroenterology, 2007; 54(76); 1276-79
28.. Giuiliano E, Paolino D, Fresta M, Cosco D, Mucosal applications of poloxamer 407-based hydrogels: An overview: Pharmaceutics, 2018; 10(3); 159
Figures
Tables
 Table 1.. Laboratory test results of our patient. The tests were performed at the time of the initial, first, and second follow-up gastroscopies.
Table 1.. Laboratory test results of our patient. The tests were performed at the time of the initial, first, and second follow-up gastroscopies. Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions.
Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions. Table 1.. Laboratory test results of our patient. The tests were performed at the time of the initial, first, and second follow-up gastroscopies.
Table 1.. Laboratory test results of our patient. The tests were performed at the time of the initial, first, and second follow-up gastroscopies. Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions.
Table 2.. Pathogeneses of Cameron lesions. Each factor is accompanied by a short explanation of its significance and role in the development of Cameron lesions. In Press
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942824
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.943118
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942826
14 Mar 2024 : Case report 
Am J Case Rep In Press; DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.942770
Most Viewed Current Articles
07 Mar 2024 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.943133
Am J Case Rep 2024; 25:e943133
10 Jan 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935263
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935263
19 Jul 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.936128
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e936128
23 Feb 2022 : Case report 
DOI :10.12659/AJCR.935250
Am J Case Rep 2022; 23:e935250








